
Neurotherapy, also known as Neurofeedback or electroencephalogram (EEG) biofeedback, was developed in the ’50s and ’60s. It was developed as a non-invasive, drug-free method of treating certain psychological conditions such as addiction, anxiety, depression, and so on through feedback modification and monitoring of brain waves when exposed to certain stimuli.
Table Of Contents:
- What Is Neurofeedback?
- What Are the Neurotherapy Principles?
- What Happens During a Session?
- What Are the Various NF Techniques?
- Are There Any Side Effects?
- How Much Does the Therapy Cost?
- Can Therapy Be Carried Out At Home?
- What Is the Difference Between Biofeedback and Neurofeedback?
- Is It Effective In Substance Abuse Treatment?

EEG Neurofeedback uses a monitoring device or sensor to obtain information about what is going on in the mind or body. Neurofeedback training measures and maps activity in specific areas of the brain. Information obtained from Neurotherapy devices is then used to treat addiction and other related mental health disorders.
What Is Neurofeedback?
As mentioned previously, Neurotherapy was developed as a non-invasive and medication-free alternative to conventional treatments for conditions such as anxiety, depression, chronic stress, and drug addiction. It is built around the central belief that these conditions stem from maladaptive brainwave patterns, which have been built over time and can be treated by retraining the brain to build healthier cognitive and emotional pathways using positive or negative feedback.
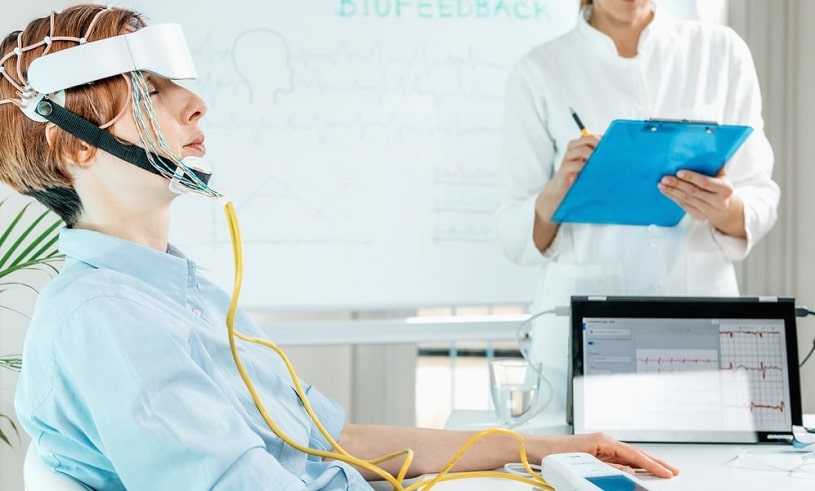

The process can be broken down into several key steps. First, an electroencephalogram (EEG) is attached to the patient’s head and continuously monitors brainwave activity in real-time. A complex algorithm monitors these patterns, identifies harmful or destructive associations, and then provides audiovisual feedback to the patient to reinforce more positive and healthy connections. Through positive reinforcement, these new connections become the dominant thinking pathways leading to healthier and less self-destructive habits over time.
What It Treats
Several Neurotherapy training protocols have been developed to help specific problems, such as:
- ADD
- ADHD
- Autism
- Anxiety
- Depression
- Sleep disturbance or insomnia
- Cognitive disabilities
- Bipolar disorder
- PTSD
- Chronic stress
- Seizures
- Migraine
- Spectrum disorder
- OCD
- Tinnitus
- Schizophrenia
- Alcoholism and drug addiction
Prolonged use of alcohol and drugs is associated with a disruption in brain activity.
Neurofeedback therapy focuses on brain activity and attempts to regulate brain function. These abnormal brainwave patterns produce symptoms such as anxiety and depression, which can trigger a relapse in recovering addicts. Thus, training helps restore healthy activity and is an essential adjunctive therapy in substance abuse recovery.
EEG Neurofeedback Principles
Brain waves therapy is based on scientific findings on human brain functioning. It was found that different parts of the human brain are active during different activities. Frequency bands called alpha, beta, delta, and theta become activated as people go about their daily activities. For example, when someone is balancing their checkbook, the beta frequency may be active. When someone is relaxing and winding down after work, alpha waves may predominate.
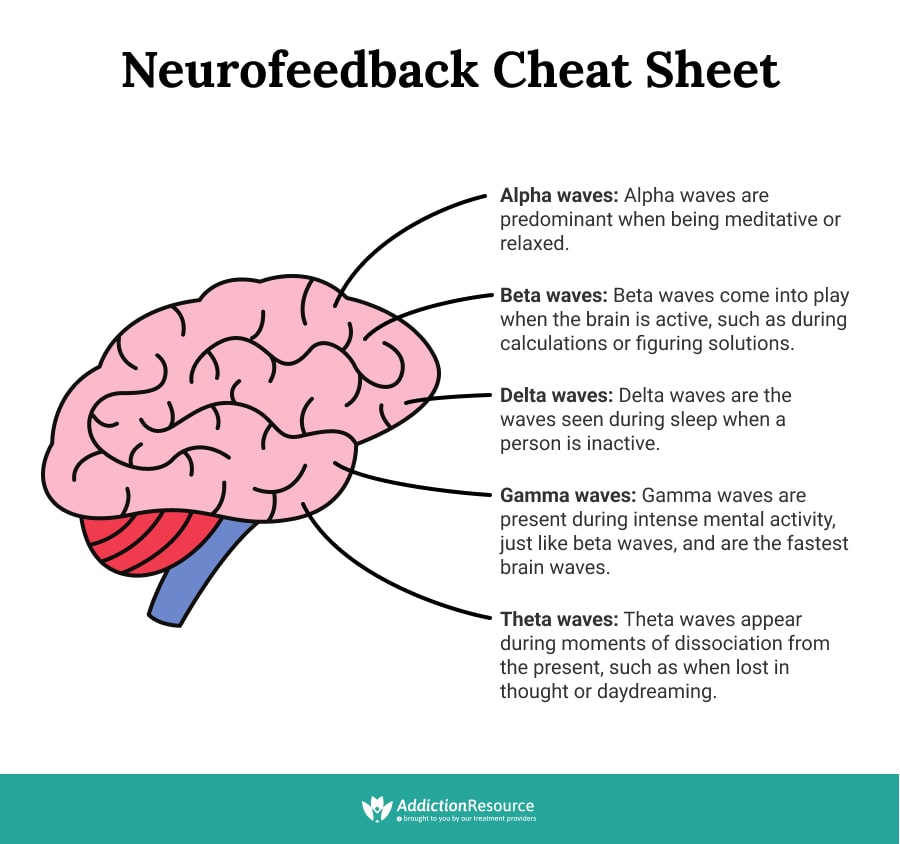
Neurofeedback therapy improves the ability of the brain to shift smoothly between the states of arousal and relaxation. The techniques identify the specific pathways that are over-or under-activated, misaligned, or dysregulated. Following this assessment, a variety of equipment is available to address the client’s particular needs. Neurotherapy training encourages healthy brain function using well-researched and proven techniques. It also addresses dysregulations in brain activity that produce symptoms, such as anxiety disorders, migraines, sleep disorders, which often accompany addictive behaviors.
What Happens During a Neurotherapy Training Session?
What is Neurofeedback training like? During Neurofeedback therapy, mental health professionals, therapists, and psychologists work with clients in one-on-one training sessions. Neurofeedback training device sensors are placed on the patient’s head to monitor brainwave activity. The EEG machine records electrical activity in the brain, detects normal and abnormal brain function, and provides real-time feedback via images or sounds.
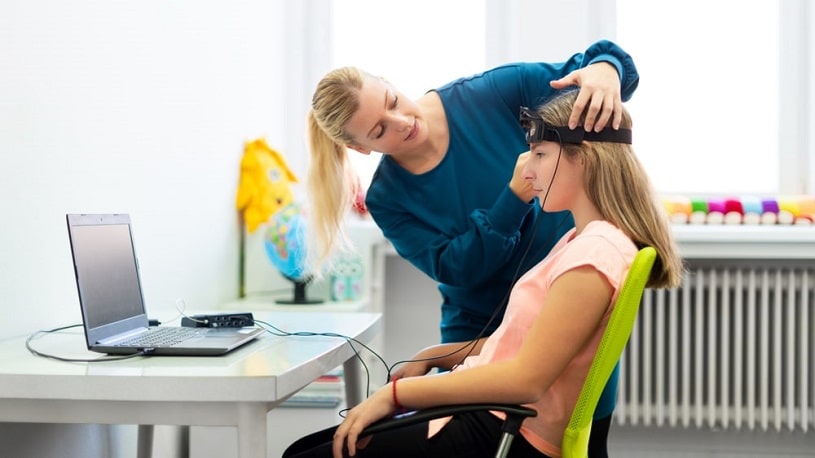

Customized relaxation and stress-relief interventions are developed based on this assessment to benefit people struggling with addiction. These Neurofeedback training techniques include meditation, breathing exercises, positive visualization, and other relaxation strategies. Essentially, the brain is rewarded for changing to appropriate wave patterns. It usually comes in the form of a simple video game, and the player is awarded in the game when the brain forms positive cognitive pathways, leading to a positive feedback loop. It boosts awareness of healthy and unhealthy thinking patterns and teaches the user how to identify and avoid negative thought processes. This gradual conditioning is a type of self-regulation.
People with substance abuse issues learn and reinforce new capabilities. In other words, healthy frequencies are promoted, and unhealthy ones are diminished. Eventually, this shapes the brain towards more regulated, aligned activity. Thus, Neurofeedback training helps the individual gain control over what is usually an involuntary function.
Neurotherapy Techniques: Training the Brain to Function Better
There are many different Neurotherapy techniques, and some of the most popular are:
CES machine
These FDA-regulated devices have been on the market since the 1950s and are proven effective and safe. CES machine is used as a drug-free, portable, cost-effective therapy that is non-addictive and appropriate for people of all ages. The device provides gentle electrical stimulation to specific areas of the brain that have abnormal functioning. Despite their proven effectiveness, the mechanism of action behind the device is largely unknown.
Research suggests that the deactivation of certain cortical and subcortical regions by mild electrical impulses ranging between 0.5-100 Hz caused significant changes to the brain’s resting state.
Deep Brain Neurofeedback
Deep brain Neurofeedback (LoRETA) is the most advanced tool used by trained Neurotherapy specialists. It addresses specific goals and produces results in fewer sessions. QEEG brain mapping allows the training program to be tailored to the addict’s brain activity and symptoms. Comparisons are made to previous QEEGs to assess progress. A comparison can also be made to a baseline Z-score to evaluate how much training is required.
Real-Time Feedback With Functional MRI
Real-time feedback with functional MRI (fMRI) can help treat addiction, depression, chronic pain, and schizophrenia. The treatment targets specific brain areas compared to pharmacotherapy, which is more like taking a shot in the dark. The technique uses real-time information obtained from magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to map our activity in the brain during certain actions and use this information for Neurofeedback therapy.
Neurofeedback Computer Games
Teenagers with addiction problems may be asked to play a computerized video game on EEG plus tablet during sessions. The game only proceeds to the next stage when the adolescent is focused and calm. If the EEG machine detects distracted brainwave patterns, the game stops. This method of reward conditions the brain to function with healthy brain activity patterns and has been shown by research to be quite effective. Research has also shown that this improves rapid visual processing, attention span, can help strategy-formulation, executive functions, and spatial working memory.
Neurofeedback Training Side Effects
Although Neurotherapy is safe and the side effects are usually rare and transient. The incidence and severity of these side effects may depend on the location of the brain being targeted, the frequencies being used, and pre-existing high-risk conditions such as seizure disorders, head trauma, narcolepsy, and migraines.
Some of These Side Effects May Include Things Such As:
- Anxiety or depression
- Headaches or dizziness
- Cognitive impairment
- Internal vibrations
- Muscle tension
- Social anxiety
- Low energy or fatigue
Neurofeedback Therapy Cost
A standard course of Neurotherapy treatment can cost about $1500. A single session can cost a patient $100 and up. In the long run, Neurotherapy sessions enhance the brain’s capacity to function well, but some conditions can be prohibitive in terms of cost. In such situations, it is possible to undergo supervised home sessions after a series of in-office training sessions. It allows the patient to receive frequent, consistent therapy that is affordable and convenient.
Can One Do Neurofeedback At Home?
Neurotherapy can be effectively carried out at home using internet technology and more portable Neurofeedback equipment. A specialist can successfully train patients to carry out simple exercises using Neurofeedback at home. Whether Neurofeedback at home is as effective as an outpatient appointment depends on the user’s level of skill and how well the Neurotherapy specialist taught the process. With the proper knowledge and Neurotherapy professional’s help, almost anyone can effectively carry out this technique at home.
Biofeedback vs. Neurofeedback
While Biofeedback vs. Neurofeedback may seem alike and are frequently used interchangeably and are related, they do not refer to the same concept. There are several key differences between Biofeedback vs. Neurofeedback. Biofeedback therapy refers to a form of therapy that allows an individual to monitor certain biological inputs such as body temperature, blood flow, brainwaves, heart rate, etc. Then using special techniques, the individual learns to regulate these functions through negative or positive feedback. On the other hand, NF is a subset of biofeedback that deals majorly with monitoring the electrical activity of the brain.
Neurotherapy Effectiveness For Substance Abuse Treatment
Neurotherapy is a popular and widely available therapy that should be included in treatments for drug abusers in the United States. With the use of electroencephalography (EEG) to track brainwave patterns, an addict’s response to various actions is measured. The Neurotherapy specialist then trains the recovering addict to self-regulate and obtain control over the autonomic nervous system.

Over a few decades of research and experience with Neurotherapy success rate shows promising results for addiction treatment. Neurofeedback therapy works for most people battling substance abuse problems because the human mind is designed to learn and acquire new skills. Yet, it is essential to have realistic expectations and not be discouraged by slow progress.
For most recovering addicts, the outcome of brain wave therapy techniques exceeds their expectations. In fact, for people with low expectations to begin with, the results can feel almost miraculous. The changes brought about by Neurotherapy are not miraculous but simply a harnessing of the incredible power of the human brain to adapt and recover function.
NF can be combined with other types and approaches used in addiction treatment, like the psychodynamic model or NAD+ therapy. Successful training in Neurofeedback techniques can help reduce the need for medications that regulate brain function. That is because recovering substance abusers learn to self-regulate their response to stress and other triggers of addiction to avoid drug or alcohol relapse.
The Future of Addiction Therapy
While the idea of treating addiction through the use of brainwave technology may sound far-fetched, this is fast becoming a reality in many parts of the world. NF is a great form of addiction therapy due to its effectiveness, reduced side effects, ease, and requires no pharmacotherapy. Remember, however, that Neurotherapy should only be carried out by a trained professional or under the supervision of a skilled professional.
Neurotherapy can be also used while staying at a sober living house, as it is mostly outpatient treatment. This way it will serve as a part of aftercare and will help deal with pink cloud in recovery.
Hope Without Commitment
Find the best treatment options. Call our free and confidential helpline
Most private insurances accepted
Find Drug Rehabilitation Centers Near You Anywhere In the US
Addiction Resource team has compiled an extensive list of the top drug rehabilitation facilities around the country. Use our locator tool to find the best centers near you.
Page Sources
- Banerjee, S., & Argáez, C. (2018). Neurofeedback and biofeedback for mood and anxiety disorders: a review of clinical effectiveness and guidelines.
- Feusner, J. D., Madsen, S., Moody, T. D., Bohon, C., Hembacher, E., Bookheimer, S. Y., & Bystritsky, A. (2012). Effects of cranial electrotherapy stimulation on resting-state brain activity. Brain and behavior, 2(3), 211–220.
- Brühl A. B. (2015). Making sense of real-time functional magnetic resonance imaging (rtfMRI) and rtfMRI neurofeedback. The international journal of neuropsychopharmacology, 18(6), pyv020.
- Jirayucharoensak, S., Israsena, P., Pan-Ngum, S., Hemrungrojn, S., & Maes, M. (2019). A game-based neurofeedback training system to enhance cognitive performance in healthy elderly subjects and in patients with amnestic mild cognitive impairment. Clinical interventions in aging, 14, 347–360.
- Hammond, D. C. (2011). What is neurofeedback: An update. Journal of Neurotherapy, 15(4), 305-336.
- Hammond, D. C. (2005). Neurofeedback treatment of depression and anxiety. Journal of Adult Development, 12(2), 131-137.

 Reviewed by:
Reviewed by:  Written by:
Written by: 










 FindTreatment.gov
FindTreatment.gov