The side effects of stimulants are both short-term and long-term and are largely depended on the drug itself. As one of the short-term side effects of stimulants on the brain, users may experience a heightened level of focus and energy because of the increased levels of dopamine, which may be desirable until the drug wears off. Conversely, the long-term effect of stimulants on the body may be adverse, and it is, therefore, advisable that anyone abusing any of these substances and is already addicted seek professional assistance.
Learn About Stimulants Side Effects:
Stimulants Effects
The abuse of these drugs is most likely synonymous with dependence and addiction due to the physiological effects of stimulants. Stimulating substances sometimes refer to uppers because of their performance-enhancing, alertness inducing, and euphoric effects on the body. On the other hand, downers (depressants) create the opposite effects of stimulating drugs. However, doctors warn about mixing uppers and downers with the intent of canceling out their effect.
Short-Term Effects Of Stimulants
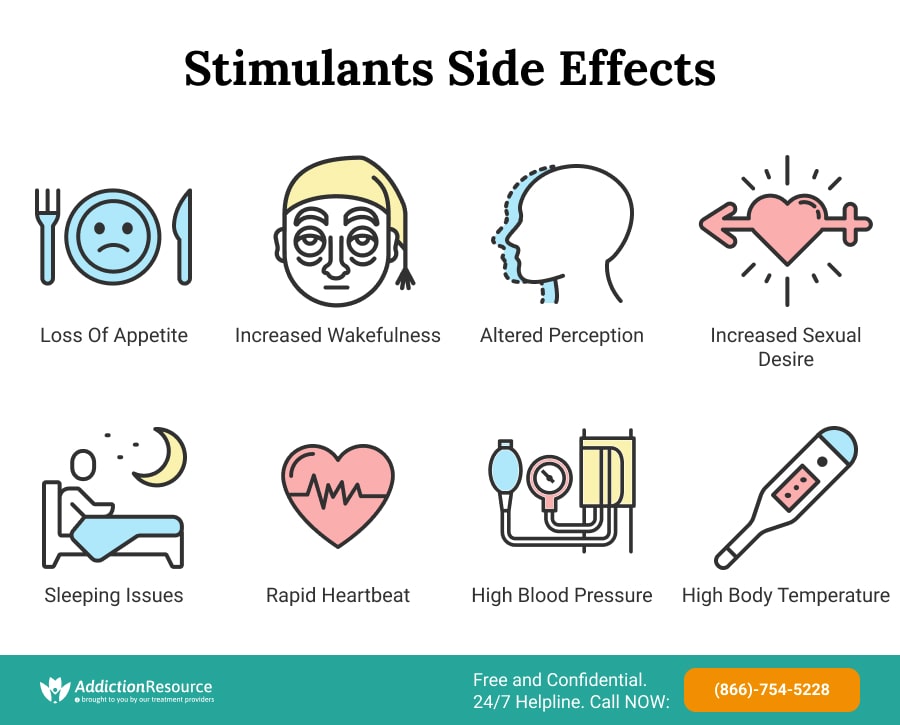
Short-term effects of stimulating drugs can have adverse effects on the user’s health. According to the US National Library of Medicine, between 30 to 50% of a sample of 158 uppers users reported some form of adverse effects in the short-term.
Some of the uppers short-term effects include:
- Loss of appetite
- Increased wakefulness and physical activity
- Improved attention
- Increased sexual desire and performance
- Interrupted sleep patterns
- Rapid/irregular heartbeat
- Increased blood pressure and body temperature
Long-Term Effects Of Stimulants
Long-term effects are those that occur beyond the short-term feelings of euphoria and wellbeing. The long-term usage may result in serious uppers side effects, as well as dependence. In fact, the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration estimated that in 2007, about 1.6 million Americans were dependent on cocaine, one of the illegal stimulants. This is out of a possible 22 million Americans over the age of 12 years who met the criteria for substance abuse or dependence.
The list of stimulants long-term effects include:
- Cardiovascular damage
- Weight loss
- Chronic exhaustion
- Breathing problems
- Cerebral Hemorrhage
- Stroke
- Seizures
- Muscle deterioration
- Extreme weight loss and malnutrition
- Psychosis
- Anxiety
The appearance of the side mentioned above effects with the concurrent use of stimulating drugs indicates that a person needs professional help. Substance abuse treatment is available in many rehab facilities.
Hypothyroidism And Stimulants
Patients with ADHD are more sensitive to hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism. Methylphenidate, (Ritalin, Concerta, & Daytrana) and Dexamphetamine (Dexedrine, Dextrostat) are some examples of stimulants for ADHD. Hypothyroidism, a condition where the thyroid gland produces fewer hormones than normal, is one of the psychostimulants side effects that is common in patients using these drugs for the treatment of ADHD. This is because uppers have a harmful effect on the thyroid gland, thereby creating a condition where the gland does not function optimally.
Stimulants And Sleep
One of the central nervous system (CNS) stimulants side effects is the alteration of an individual’s sleeping pattern. They affect the central nervous system, causing increased alertness and an induced inability to sleep. Management of excessive sleepiness disorder and lack of sleep in adults with ADHD is what stimulants do when it comes to sleep.
How Stimulants Affect One’s Sleep
One of the effects of stimulants on the body is the central nervous system arousal, causing a temporary increase in energy levels, heart rate, as well as blood pressure. Once this is done, the physical effects of stimulating drugs such as wakefulness and increased alertness begin to manifest.
Nonetheless, when used correctly, they can promote healthy sleeping patterns in the individual, but when they are abused, they can severely disrupt sleeping patterns.
Longest Time Awake With Stimulants
The longest time without sleep ever recorded with stimulating drugs was 201 hours (8.4 days), a record set by the New York DJ Peter Tripp. However, after just three days without sleep, Tripp began experiencing the negative side effects of the stimulants as well as sleep deprivation.
Why Do Stimulants Make One Clench A Jaw?
Clenching of the jaw, medically known as bruxism, has been associated with the use of amphetamines such as Adderall. This condition is one of the dangers of uppers because it may result in severe gum damage, jaw pain, and even tooth loss. Stimulating drugs have a powerful influence on an individual’s dopaminergic projections. More research needs to be done to determine the reason. However, some evidence suggests that the effects of stimulants on central nervous system neurotransmission, such as dopamine, may be the cause. As a solution, mouth guards may be used. There are also OTC stimulants such as caffeine and Theanine that can be used as Adderall alternatives.
No alternative should be used without a doctor’s consultation.
Why Do Stimulants Suppress Appetite?
Dextroamphetamine and amphetamines like Adderall cause increased the production of dopamine in the brain. Dopamine, a neurotransmitter, helps send signals when the body is satisfied with food. This is the reason why one of the stimulants side effects is weight loss from the resultant suppressed appetite.
Sensitivity To Stimulants
Sensitivity to uppers varies from one person to another. This stimulant effect on the body may be attributed to a system of enzymes called Cytochrome p450. This enzyme breaks down chemicals in the blood, including stimulating drugs such as caffeine. People have varied amounts of these enzymes; therefore, different levels of sensitivity to stimulating drugs may arise. CNS stimulant side effects are also varied because of this reason.
What To Do In A Case Of Adverse Effects
As pointed out, those are what dangerous effects stimulants could have on an individual. Some of these effects could become fatal for those abusing these drugs. In addition, people who abuse uppers regularly have been proven to develop tolerance over time, making this another danger of stimulating substance abuse because it can lead to overdose.
If there are any adverse effects on prescription stimulating drugs, it is advisable to consult a doctor and inform them of these effects of the stimulant on the body. Furthermore, people who are abusing any form of stimulating drugs either for performance enhancement or increase attentiveness should seek professional help in the drug rehabilitation centers because of not only the legal consequences of drug abuse but also the adverse effects it has on one’s health.
Page Sources
- Williamson S, Gossop M, Powis B, Griffiths P, Fountain J, Strang J. Adverse effects of stimulant drugs in a community sample of drug users. Drug and Alcohol Dependence. 1997; 44(2-3): 87-94. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9088780.
- Overcoming cocaine or stimulant addiction. Harvard Mental Health Letter. Harvard Health Publishing. 2009. https://www.health.harvard.edu/newsletter_article/Overcoming_cocaine_or_stimulant_addiction.
More About Stimulants:

 Authored by
Authored by  Reviewed by
Reviewed by