Quite a number of people usually use the term antihistamine to describe drugs used for the treatment of allergies. However, medical practitioners such as doctors, pharmacists, and other scientists use the term for describing a class of drugs that antagonizes the activities of histamine receptors present in the body. There are some specific biological receptors on the human cells. These receptors are called Histamine receptors. Therefore, antihistamines refer to drugs that bind to these receptors to oppose their natural roles.
Table Of Contents:
- What Is an Antihistamine?
- What Are Antihistamines Legal Classification?
- Antihistamines Classification by Generation
- Antihistamine Classification by Drug Formulation
- What Are the Potentials for Antihistamine Abuse?
- Who Are the Antihistamine Abuse Risk Groups?
- Effects of Antihistamines Abuse
- What Is Antihistamine Addiction?
- What Are the Treatments for Antihistamine Addiction

What is an antihistamine? This article tackles how to end antihistamines addiction through understanding the problem and seeking timely professional treatment.
What Is an Antihistamine?
Antihistamines are the medications that help to alleviate these allergies. Some antihistamines also help with some gastric problems, anxiety, and a lot more. In this regard, antihistamines are hereby classified based on the particular histamine receptor upon which they act.
What Are Antihistamines Legal Classification?
The medication is classified into first and second-generation types, and both types come in different forms.
The first generation, being the most potent, has a strong sedating effect and is categorized as a schedule II and schedule III drug.
This is because they affect the CNS and have a low potential for addiction. The drug is legally unfit for use in the treatment of children under the age of 2 years. The first-generation are mostly classified as sedating types. Prescription antihistamines are usually provided after a proper medical checkup. In some cases, it may be easy to obtain antihistamine over the counter, especially generic versions with a shorter half-life.
What Are Over-the-Counter Antihistamines?
The medication is available and obtainable at local stores for quick relief from various sudden allergic reactions such as eye allergies, severe itches, and others, and they are considered to be much milder with lesser side effects. Finding the best OTC antihistamine depends on what form of the medication suits the condition best. There are OTC antihistamine eye drops, capsules, sprays, and others.
Purchasing over-the-counter antihistamines for hives may be safer after medical counseling. Some of these medications are safer under prescription as they are more potent and can cause secondary health issues when taken the wrong way, especially in certain health conditions. There are allergies that may require one of the most potent medications and in some cases, the mildest. This can only be determined by a professional to avoid severe antihistamine side effects.
Here Are a Few of the Strongest Over-the-Counter Brands Available:
- Tavist
- Dimetane
- Benadryl
- Alavert
- Claritin
- Zyrtec
What Are Prescription Antihistamines?
Why do doctors prescribe this medication? There are many conditions where this medication serves as the first option for medication. These medical conditions include sedation, allergic conjunctivitis, hives, allergic rhinitis, itching, motion sickness, anxiety, anaphylaxis, and others.
Medical experts are in the best position to prescribe the safest antihistamine in pregnancy. It is also imperative to make sure that no other medication has the active ingredient in the antihistamine recipe as this may result in too much antihistamine in the system.
Here Is a Brand Prescription Antihistamine List:
- Optivar
- Palgic
- Clarinex
- Emadine
- Astelin
- Xyzal
- Atarax
- Livostin
- Astepro
Antihistamines Classification by Generation
Antihistamines, after its discovery in 1936 and its subsequent application in the management of asthma, became a popular medication for the treatment of allergies. In 1942 the second class of these medications were developed with lesser toxicity and were more potent. Other functions for the drug were discovered in 1947 and beyond. There are two main categories for antihistamine classification: the first generation and second generation.
The first subtype is called H-1 receptor antagonists, otherwise called H1 receptor blockers. First-generation – the first generation can be classified into five main groups and other derivatives. The five groups are ethanolamines, alkylamines, piperazines, ethylenediamine, and phenothiazines. These classes are natural sedatives and affect the CNS and periphery due to its high solubility in lipids.
Some First-Generation Types Are:
- Promethazine
- Diphenhydramine
- Clemastine
- Antazoline
- Cyclizine
- Chlorpheniramine
- Doxylamine
- Meclizine
The second subtype is called H-2 receptor antagonists, otherwise regarded as H2 receptor blockers. They are commonly used in the treatment of gastrointestinal conditions such as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), peptic ulcer disease, gastritis, motion sickness, nausea, vomiting.
Common Examples of H-2 Antihistamines Are:
- Cimetidine
- Famotidine
- Lafutidine
- Nizatidine
- Ranitidine
- Roxatidine
- Fexofenadine
H-3 receptor antagonists, otherwise called H3 receptor blockers, are a classification of antihistamines that act on H-3 receptors. These receptors are primarily found in some brain cells. H-3 histamine antagonists have stimulant and cognition-modulating effects.
Examples of selective H-3 antihistamines include Clobenpropit, ABT-239, Ciproxifan, Conessine.
H-4 receptor antagonists inhibit the activity of the H4 receptor. An example of this subclass is thioperamide.
Antihistamines Classification by Drug Formulation
Allergy medications come in various forms depending on the route of administration. The reason behind a specific route of administration is to ensure that the drug becomes effective in the shortest period via various channels. Antihistamine decongestant medication, whether pills, liquid, or nasal spray, are usually administered as quick and temporary relief of sinusitis and nasal congestion. Here are some major classifications based on the route of exposure.
Antihistamine Pills
Most of the otc drugs or prescription medication works best for swellings, runny nose, severe itching, and watery eyes. Pills are also the most effective antihistamine for hives. It is usually advised that persons on this medication should neither drive or operate heavy machinery as the drug causes drowsiness. Those that cause drowsiness are specifically Diphenhydramine and Chlorpheniramine.
The Non-drowsy Over the Counter Pill Brands Are:
- Loratadine (Claritin)
- Cetirizine (Zyrtec)
- Fexofenadine (Clarinex)
- Levocetirizine (Allegra)
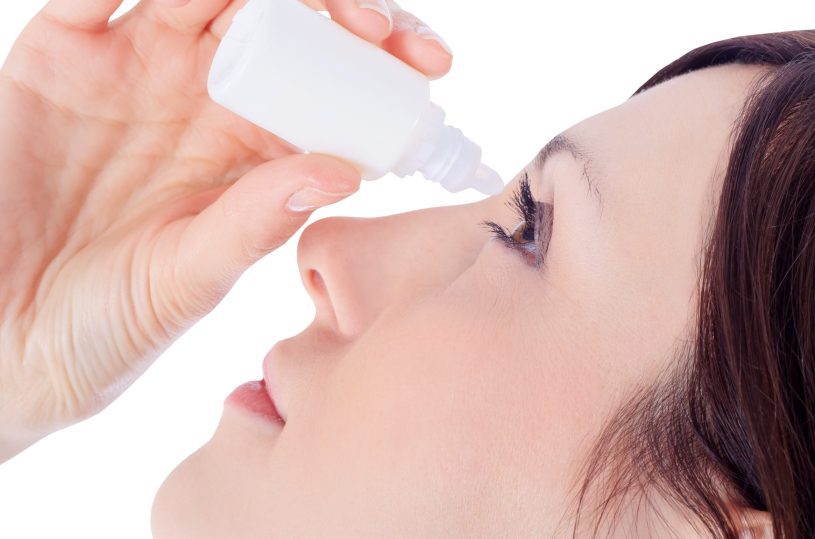
Eye drops
The eyes are often easily susceptible to irritation and allergies due to dust and other sediments.
Antihistamine eye drop otc relieves itchiness, redness, and swollen eyes. Over-the-counter antihistamine eye drops are often combined with other ingredients to improve its efficacy.
Some Examples of the Most Potent Antihistamine OTC Eye Drops Are:
- Ketotifen (Alaway)
- Pheniramine (Visine A)
- Azelastine (Optivar)
- Emedastine (Emadine)
- Olopatadine (Patanol, Pataday)

Nasal Sprays
Uses of over-the-counter antihistamine nasal spray include itchy and runny nose, sneezing, postnasal drip, sinus congestion. Usually, this medication is available by prescription.
Antihistamine Nasal Spray Prescription Brands Include:
- Olopatadine (patanase)
- Azelastine (astepro)
Creams
Topical allergy meds relieve allergic reactions such as itchy skin, swelling, inflammation, sneezing, watery eyes, and other irritations.
Antihistamine cream over the counter can also be applied in the treatment of allergic rhinitis, inflammation, and stings from insect bites, cuts, burns, and reactions caused by poisonous plants.
Some Highly Effective Topical Medications Are:
- Zonalon (doxepin)
- Prudoxin
- Benadryl (diphenhydramine)
What Are the Potentials for Antihistamine Abuse?
The abuse of Antihistamine is on the rise alongside many other over-the-counter medications. Perhaps, this is because they are considerably cheap and easy to procure. These allergy medications appear to be harmless. They are used for treating allergic reactions, but unfortunately, the potential abuse of antihistamines for the sedative effect is becoming more common today. Thus, it may require stricter regulations to curb its abuse. Both the users and their loved ones must be aware of this risk.
Histamine is released by the body, mainly during allergic reactions and to some extent during certain viral infections like a common cold. When histamine binds to its specific receptors on the cell surface, it stimulates changes within the cells. These changes are responsible for the symptoms such as sneezing, itching, increased nasal discharge, and so on.
Antihistamine medications are usually taken to relieve these symptoms. While they do so, they can produce sedative effects. Some people may also combine them with other substances which act in synergy to potentiate the symptoms of one another.
Users easily assume that antihistamine medications are safe to use because they are easily accessible. However, they can still cause adverse effects and even death when largely abused. To reduce the risk of having side effects from antihistamines overuse, users must carefully follow all dosage directions.
Users are advised to know the symptoms of antihistamines overdose and seek help in stopping their acts of antihistamine abuse.
What Are Antihistamine Abuse Risk Groups?
It is often said that people who abuse antihistamines have the tendency to be an abuser of other substances such as alcohol, nicotine etc. These categories of people are classified as risk groups.
These Risk Groups Include:
- Those genetically predisposed to addiction
- People with brain characteristics that make them vulnerable to addictive substances
- Those who are highly impulsive
- Individuals with mental health or behavior disorders
- People who have suffered physical, emotional, or sexual abuse
- Those who have addiction in the family or amongst their peers
- Anyone who started using alcohol with antihistamines, or nicotine, or other drugs at an early age
- People who display aggressive behavior, especially at a young age
- Children and teens who lack parental supervision
- Those living in poverty
However, because these are easy for nearly anyone to access and they expectant as safe, people who are averse to abusing other substances may be open to the idea of trying to get high on allergy medication. This means that even if someone does not belong to an at-risk group, the risk is still presented.
Effects of Antihistamine Abuse
The signs of antihistamine abuse may not be initially obvious. However, with time, overt features may begin to appear. The features observed are due to its effect on some systems of the body. The body system commonly affected is the central nervous system which is mainly the brain and spinal cord. The physical and psychological symptoms that may be seen are highlighted below.
Psychological Signs and Symptoms of Antihistamines Abuse
There could be visible psychological signs observed in abusers of antihistamines.
They Include:
- Anxiety
- Depression
- Drowsiness
- Restlessness
- Confusion
Physical Signs and Symptoms of Antihistamines Abuse
There could be visible physical signs observed in abusers of antihistamines.
Some of Which Include:
- Loss of appetite
- Physical weakness
- Chest tightness
- Headache
- Gastrointestinal distress
From the foregoing, it is evident that antihistamine abuse has a myriad of symptoms and these symptoms are multi-systemic.

What Are the Social Effects of Antihistamines Abuse?
The social effects of abusing antihistamine medications are quite similar to those abusing any other psychoactive substances. The users may change social groups to be around others who abuse substances and find themselves pulled into abusing drugs that are more addictive and more dangerous. Often, the social ramifications of abuse are the hardest to cope with.
They Include:
- Poor interaction with others
- Disconnection from families
- Solitary lifestyle
- Loss of occupation
- Threat to their security
- Damaged reputation
- Stigmatization
They may change their familiar companions in order to associate more with other substance abusers.
What Is Antihistamine Addiction?
Substance abuse is dangerous. It doesn’t necessarily mean a mere impact on a person’s life. It is more complex. One common feature is that the abusers find it difficult to stop anytime they want to. They usually lack the willpower to stop these acts on their own. If it gets to this point, then addiction is imminent. Addiction could be physical or psychological.
Antihistamines Psychological Addiction
It is also possible for someone to become psychologically addicted. This can occur with or without physical addiction. In this case, the user feels mentally compelled to abuse the medications. They may become apprehensive and afraid of what will happen to them without using the medications.
Antihistamines Physical Addiction
Physical addiction to allergy medication is unlikely, but it is possible when taken at high doses and abused for a long period. The first step in physical addiction is antihistamine tolerance. This occurs when the body becomes used to the presence of the drugs in the body, and the effects of the medication are no longer felt at the same strength.
From there, dependence can develop. This means that the body struggles to function normally without the medication. At this point, addiction can quickly develop. Users may feel physically compelled to seek out the medication and experience antihistamine withdrawal when they do not take the drug.
Antihistamine withdrawal symptoms may not be lethal but are very uncomfortable for the user and people around the user. Withdrawal symptoms such as itching, insomnia, sweating, restlessness to mention a few, may return and may be very severe. Any user at this stage needs urgent help. A person addicted to a substance like Diphenhydramine may find it very difficult to stop the act all alone.
Antihistamine Addiction Treatment
Drug rehabilitation centers across the country offer antihistamine abuse treatment. These centers can help users detox, find ways to cope with their urges, and even help them find alternatives, such as a natural antihistamine for hives, which cannot be abused. The goal is to set up the user to be physically and mentally strong enough to resist temptation going forward and live a better life.
Getting help starts with finding the right treatment center. All this takes is a quick search online. Once the right rehab center is located, users just need to give them a call and learn how to enroll in their antihistamine abuse recovery program.
Hope Without Commitment
Find the best treatment options. Call our free and confidential helpline
Most private insurances accepted
Page Sources
- Preventing Drug Use among Children and Adolescents (In Brief). National Institute on Drug Abuse. https://www.drugabuse.gov/publications/preventing-drug-abuse-among-children-adolescents/chapter-1-risk-factors-protective-factors/what-are-risk-factors
- Antihistamines for allergies. MedlinePlus. U.S. National Library of Medicine. https://medlineplus.gov/ency/patientinstructions/000549.htm
- Emanuel MB. Histamine and the antiallergic antihistamines: A history of their discoveries. Clin Exp Allergy. 1999;29:1–11. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1046/j.1365-2222.1999.00004.x-i1
- Doyle WJ, Boehm S, Skoner DP. Physiologic responses to intranasal dose-response challenges with histamine, methacholine, bradykinin, and prostaglandin in adult volunteers with and without nasal allergy, J Allergy Clin Immunol, 1990, vol. 86. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0091674905801563
- Gwaltney JMJr, Druce HM. Efficacy of brompheniramine maleate treatment for rhinovirus colds, Clin Infect Dis, 1997, vol. 25 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9402380/

 Authored by
Authored by  Reviewed by
Reviewed by