Individuals experiencing pain symptoms have several options to opt for when it comes to finding relief. Norco has become a widespread product among the US population, combining acetaminophen and hydrocodone bitartrate for a more potent alleviation of pain symptoms. Hydrocodone remains one of the most commonly prescribed types of opioids in the country. Norco headache relief, joint pain alleviation, and the use of the product for other symptoms may yield side effects. Individuals who are looking to use the medicine should understand the side effects of Norco. While some Norco side effects may be mild, there are more serious adverse health effects to be noted as well.
Table Of Contents:
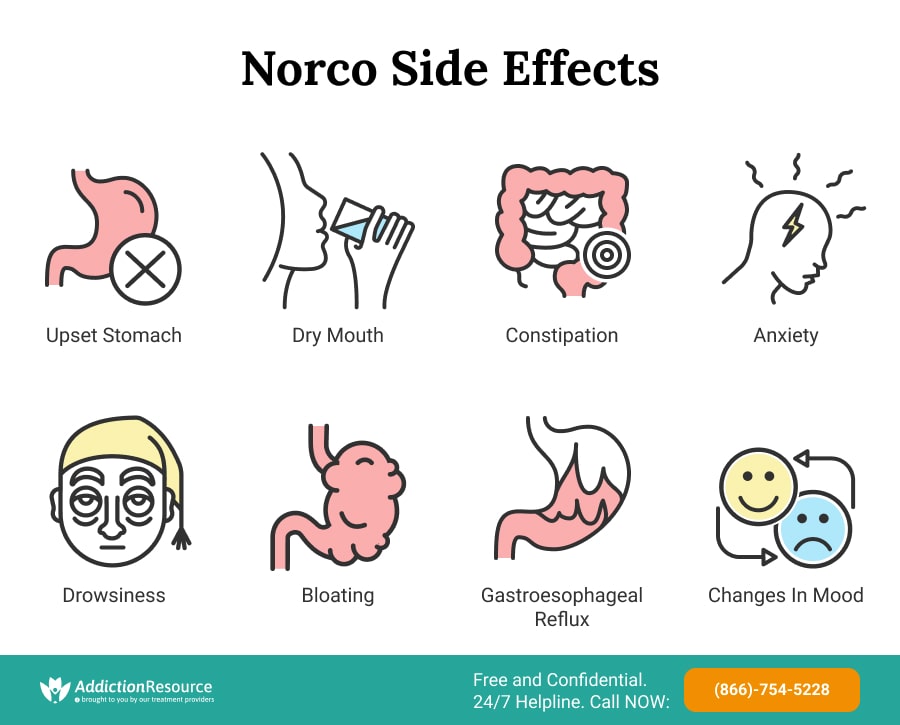
Norco Common Side Effects
Some side effects of Norco 5-325 and other strengths that the drug comes in are more common among people who use the medicine than others. The most common side effect among patients who use the drug seems to be lightheadedness.
Those Who Take Norco May Also Experience These Side Effects:
- Upset stomach
- Headaches
- Changes in mood
- Anxiety
- Drowsiness
- Norco Nausea, sometimes vomiting
- Vision may become blurry
- Dry mouth
- Constipation
- Dizziness
- Ringing sensation in the ears
In addition to considering these adverse reactions, individuals also need to consider Norco drug interactions. When this medicine is taken along with certain drugs, Norco side effects may become more severe.
Specific contraindications also exist, where the drug may lead to adverse effects if the person suffers from a particular health condition.
Long-Term Side Effects of Norco
Those who take a higher dose of the drug should consider some of the rarer adverse reactions. Some of the less common adverse effects of Norco may be harmful to the body.
Effects on the Gastrointestinal System
The use of opioids, including this particular drug, may also cause side effects on the gastrointestinal system. Various complications can develop when a person’s gut is affected by these side effects. When opioids cause issues with this particular system, it is often referred to as opioid-induced bowel dysfunction.
Possible Symptoms of Opioid-Induced Bowel Dysfunction May Include:
- Hard stool
- Incomplete evacuation when passing stool
- Anorexia
- Norco Nausea
- Vomiting
- Constipation
- Delayed digestion
- Bloating
- Abdominal pain
- Gastroesophageal reflux
Research has shown a relatively small degree of dose-dependence that comes with the prolonged use of medications that have acetaminophen/hydrocodone. The use has been associated with a particularly increased risk of patients getting gastrointestinal bleeding. This can happen even without an overdose happening. Although, this is also dependent on pre-existing GI risk factors. Generally, patients prescribed over 2.6 g/day were at higher risk of GI bleeding than those who didn’t.
Effects on the Liver
Even though Acetaminophen is harmless when it’s taken in low doses, it can be dangerous to health if the user uses too much of it. One of the main dangers of taking the medication is that too much of the Acetaminophen’s metabolite, NAPQI, can cause the glutathione pathway to get overwhelmed with NAPQI. Too much of it can be toxic for the liver and cause damage.
Effects on the Brain
Painkillers like Acetaminophen, aren’t drugs that people use recreationally, they’re not even required to be prescribed by a doctor, which is why it’s hard to think of them having a significant effect on the patient’s health or the brain. However, Acetaminophen is a component that’s present in addictive opioids like Vicodin and Percocet.

In a 2011 study, it was found that Acetaminophen doesn’t just hinder physical pain, but somehow emotional pain as well. Sixty-two subjects were given either an acetaminophen/ hydrocodone or a placebo pill. Those who took Acetaminophen showed that they were feeling less hurt than those who took the placebo pill. In another study, MRI scans were done of the brains of subjects taking Acetaminophen, and they showed decreased activity in parts of the brain that respond to emotional stress. These have shown a literal decrease in emotional pain.
Heightened Pain Sensitivity
Heightened pain sensitivity or opioid-induced hyperalgesia is when a patient that’s being given opioids for pain management, instead of feeling less pain overall, ends up being hypersensitive to pain instead. This could mean that they could even find something as small as a prick to the finger extremely painful. It happens because when a patient takes opioids, the parts of their brain that block pain get activated. Prolonged use means that the body will start fighting back and overcompensate by creating new pain signals to feel pain. This process is also known as neuroplasticity. Because of this, the patients end up with heightened pain sensitivity.
Overdose
Acetaminophen and Hydrocodone are ingredients that can cause adverse health effects and an overdose if taken in large doses. It’s essential that the patient can recognize what an overdose may look like so they can contact their doctor and seek emergency medical help immediately.
Symptoms of a Norco Overdose Include:
- Bluing of the lips and fingertips
- Breathing problems
- Cold and clammy skin
- Decreased level of consciousness or even a coma
- Increased confusion and dizziness
- Drowsiness and overall fatigue
- Lightheadedness
- Rashes and itching
- Liver failure
- Low blood pressure
- Seizures
- Stomach or intestine spasms
Allergic Reaction to Norco
Understanding the fact that Norco allergy occurs in some patients is essential. The allergy can develop during the Norco half-life, as the drug will remain more active in the system. Experiencing an allergic reaction to the drug can be dangerous. This is why issues like and itching should be taken seriously when taking drugs like this one.
Symptoms That May Develop If a Person Is Experiencing an Allergic Reaction After Taking the Drug May Include:
- Breathing difficulties
- Hives
- The individual’s face may become swollen
- Swelling in the throat, which further makes breathing and swallowing difficult
- The tongue and lips may also increase in some cases
An allergic reaction to Norco needs to be treated quickly to avoid potentially life-threatening complications from occurring.
When a person notices these symptoms associated with an allergic reaction, they should ensure they get to a medical treatment facility, such as an emergency department, as soon as possible.
Is Norco Safe During Pregnancy?
Many mothers will be concerned about whether there are safety factors in taking this drug while pregnant. Keeping in mind that the medication in question contains two different drugs, there is a possibility of being affected by opioids or Acetaminophen.

Risks for a Fetus
Know that when taking Norco while pregnant may not result in the following harm to a baby. However, these are real risks. “Drug Interactions at the Human Placenta: What is the Evidence” is just one of the studies conducted about risks for the fetus. A study on how any prescription medication affects the placenta suggests there are risks.
These Risks Are:
- When the baby is born, there’s the risk of neonatal abstinence syndrome. Withdrawal treatment for the newborn may be necessary.
- Congenital disabilities can occur, such as brain, spine, and spinal cord disorders.
- The baby may be born with heart problems.
- Risk of miscarriage or stillbirth.
- Respiratory depression in the newborn.
- Poor growth, stillbirth, premature birth, and the possibility of having a c-section are all genuine risks associated with taking it while pregnant.
Acetaminophen is considered safe to use. Research hasn’t been found to indicate it would cause significant malformations in a fetus. When it comes to studies involving animals, there is also no evidence that proves that there’s any effect on the fetus. Not enough clinical trials on mothers and fetuses have been done to determine outcomes at this point. However, when rats were tested, the consequences resulted in low weight and bone issues.
Taking Norco While Breastfeeding
Taking this drug while breastfeeding is usually not recommended. A database report by LactMed on drugs and lactation says there are Norco side effects that are harmful to the baby. While breastfeeding, this type of medication is not recommended, especially for women who have HIV or have also been taking illegal drugs. Both Hydrocodone and Acetaminophen are excreted into human milk.
Risk Of Norco Tolerance And Addiction
Norco side effects long-term can mean damage to internal organs like the liver and lead to the development of addiction. In such a case, when the person stops using the drug, they will likely suffer from withdrawal symptoms.
That is why the person might need to consider undergoing detoxification at one of the drug treatment centers. These facilities are equipped with experts who understand what the side effects of Norco are.
There are different treatment approaches for substance abuse in people who are addicted. An initial consultation with an intake counselor will help determine what type of program will be best suited for the individual. In some cases, undergoing treatment through an inpatient setting might be required. This is usually when the addiction is more serious. The patient needs to be monitored during the detoxification process and when the person is at a high risk of relapse.
Frequently Asked Questions
Does Norco Make You Sleepy?
Yes, when you take this drug, it is possible that the way it reacts to your body makes you extremely sleepy. That is why doctors recommend that you don’t drive or consume alcohol or other sedatives while taking it.
Does Norco Make You Itch?
Although itching isn’t a usual side effect of taking it, some people can develop an allergic reaction to Norco. An allergic reaction can give you hives, itching, and swelling on your tongue and throat. If this happens, contact your doctor and seek emergency medical attention immediately.
Does Norco Cause Weight Gain?
Rapid weight gain is a very rare side effect of Hydrocodone. If you’re experiencing weight gain while taking it, alert your doctor and get emergency medical help immediately.
Hope Without Commitment
Find the best treatment options. Call our free and confidential helpline
Most private insurances accepted
Page Sources
- Nataraj, N., Zhang, K., Guy, G. P., Jr, & Losby, J. L. (2019). Identifying opioid prescribing patterns for high-volume prescribers via cluster analysis. Drug and alcohol dependence, 197, 250–254. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30875645/
- Leppert W. The impact of opioid analgesics on the gastrointestinal tract function and the current management possibilities. Contemp Oncol (Pozn). 2012;16(2):125-131. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3687404/
- Rubinchik-Stern M, Eyal S. Drug Interactions at the Human Placenta: What is the Evidence?. Front Pharmacol. 2012;3:126. Published 2012 Jul 9. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3391695/
- Levonorgestrel, I. (2006). Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed)[Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Library of Medicine (US). https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK501225/
- Heard KJ. Acetylcysteine for acetaminophen poisoning. N Engl J Med. 2008;359(3):285-292. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2637612/
- Bannwarth, B. (2004). Gastrointestinal safety of paracetamol: is there any cause for concern?. Expert opinion on drug safety, 3(4), 269-272. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15268644/
- Dewall, C. N., Macdonald, G., Webster, G. D., Masten, C. L., Baumeister, R. F., Powell, C., Combs, D., Schurtz, D. R., Stillman, T. F., Tice, D. M., & Eisenberger, N. I. (2010). Acetaminophen reduces social pain: behavioral and neural evidence. Psychological science, 21(7), 931–937. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20548058/
- DeWall C. N. (2011). Hurt feelings? You could take a pain reliever... Harvard business review, 89(4), 28–29. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21510517/
- LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases; 2012-. Acetaminophen. [Updated 2016 Jan 28]. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK548162/
- Lee, M., Silverman, S. M., Hansen, H., Patel, V. B., & Manchikanti, L. (2011). A comprehensive review of opioid-induced hyperalgesia. Pain physician, 14(2), 145–161.https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21412369/
- Hydrocodone and acetaminophen overdose, https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/002670.htm

 Authored by
Authored by  Reviewed by
Reviewed by 