When used in moderation and as directed by qualified medical personnel, Methadone use is vital in the treatment of chronic pain and addiction to opioids. However, the drug poses some risks to the body, and when someone takes more than the recommended amount, they can suffer from a Methadone overdose. Methadone side effects on the body vary in severity. Some of these can be mild and can be attended to by a doctor in due time. However, other opioid side effects are very severe and need emergency medical attention.
Table Of Contents:
Read on to find out more about the Methadone effects and how they can be avoided or treated.
Short-Term Side Effects
Although Methadone (brand name Dolophine) is used to treat opiate addiction, it is an opioid itself. As a result, Methadone side effects are similar to those of opioid drugs. Even though the drug has some positive and beneficial uses, it can cause some adverse health effects when people use it. Some of the dangers of taking Dolophine can appear as soon as a person starts taking the medication, and they can last a short time.
These Short-Term Methadone Effects Include:
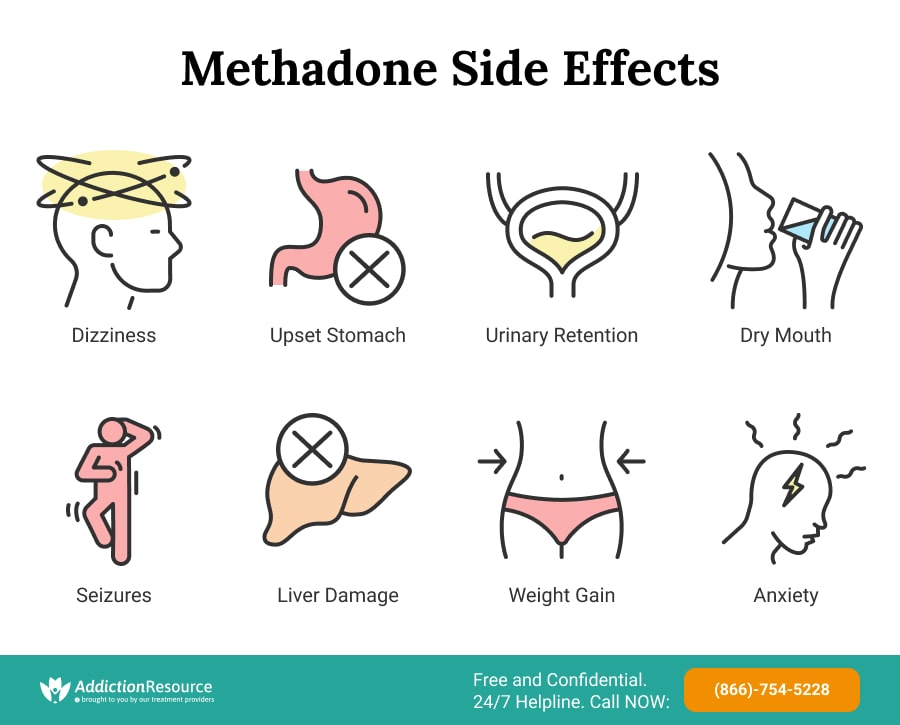
- Dizziness
- Stomach upsets
- Constipation
- Urinary retention; an inability to properly pass urine
- Dry mouth
- Skin lesions which is one of the signs of Methadone use
- A feeling of lightheadedness
- Slight tremors across the body
- Irregular heartbeat
- Seizures
- Confusion and hallucinations
- Respiratory problems like shallow breathing
- Lethargy; a sense of being tired and lazy all the time
These Methadone side effects can be reported early to the doctor to get relief so that the patient can continue taking the medication to get the benefits that it offers.
Effects of Long-Term Methadone Use
Some of the side effects of Methadone do not show up early when a patient is taking the medication. Instead, they build up over time and affect the person over a long time. The effects of long-term Methadone use can be divided into what the drug does physically to the body and its impact on the patient’s mind. Here is what the use of Dolophine can do to the body in the long run.
These Physical Side Effects of Long-Term Methadone Use Include:
- Damage to the liver
- Sexual problems in men in the form of erectile dysfunction
- Women experience issues with their menstrual cycle
- Weight gain
- Edema
- Nerve damage
- Mild tooth decay
Psychological health effects:
- Impulsivity and risky behavior
- Anxiety
- Depression
- Irritability
- Addiction if the drug is abused
- Withdrawal symptoms when the medication is suddenly halted
How It Affects The Brain
This opioid similarly affects the brain, like the more potent opioid agents whose addiction a person is trying to recover from. What sets this drug apart from the addictive ones is that it stays longer in the body. It persists for about 1 to 2 days after taking the last dose.
With this lengthy period, it can cause less tolerance. Just like the addictive opioid drugs, it binds to the mu receptors in the brain. This brings about the painkilling effect as well as feelings of sedation, relaxation, and euphoria.

Because this medication is less potent than addictive drugs, patients might abuse it for long to elicit the same response as the addictive narcotic drugs like morphine and heroin. It can cause long-term Methadone effects on the brain.
Methadone and Pregnancy
Addiction to drugs is not only a common concern among the general population. Many pregnant women are suffering from a substance abuse disorder too. One study reports an increasing problem regarding heroin addiction in pregnant women.
Several treatment options have been suggested for pregnant women with addiction problems. Studies have shown that Methadone and pregnancy can be one combination to consider. A rehab program may indicate the use of the drug as a treatment option too. This is because there seems to be a high success rate when a pregnant woman receives addiction treatment with Dolophine.
One study considered 2993 cases of birth among women getting treatment with this drug at the time of delivery. A delay in antenatal services was reported among mothers who entered a treatment program at a later period. Neonatal outcomes were also considered better among women treated with it during their pregnancy.

The study concluded that Methadone and pregnancy are a more appropriate option than maintaining an addiction to heroin. Thus, when a patient is addicted to heroin and requires medical treatment, then being pregnant on Dolophine is an option that treatment providers should consider.
Dangers Of Dolophine Use In Pregnancy
When Methadone side effects on babies are considered, a woman will have more knowledge on the subject and realize what they should expect. The baby born on Dolophine had a higher chance of premature delivery. It significantly increased the risk of morbidity among newborn babies.
The study does note that women should not consider getting off the drug during pregnancy. The risk of returning to drug abuse is too significant and can cause more severe harm to the unborn baby.
Methadone Overdose
It is possible to overdose on the medication. Because of the conditions that the drug is indicated for, it has a high ability for misuse and overdose.
In other words, patients who suffer from chronic pain can use more of this medication if they feel that they need more to kill the pain. The same also applies to patients under Methadone management treatment to overcome addictions to other narcotic drugs.
Since this drug is a narcotic, the recovering opioid addicts take more of the medication to replicate similar sedative and euphoric effects conferred onto them by the more addictive opioids like heroin.
In 2017, the Center for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) released a report that indicated that of all opioids used for pain management, Methadone made up only 1 percent. However, when it came to misuse and overdose of narcotic analgesics, the drug accounted for 23 percent of deaths.
As expounded in the CDC report, one of the reasons for death is that the medication stays in the patient’s body for a long time even after the painkilling effects are no longer being felt.
Additionally, Methadone overdose can also occur if the patient takes the drug alongside other drugs like morphine, oxycontin, and hydrocodone.
How Much It Takes To Overdose
When someone is suffering from moderate to severe chronic pain, doctors usually prescribe an average Dolophine dose of 2.5 milligrams to be administered every 8 to 12 hours. The dosage increases every 3 to 5 days. Furthermore, if the patient is trying to recover from opioid addiction, they are given 20 milligrams to 30 milligrams of the medication – taken twice a day.
So, how much will cause Methadone overdose? If the patient is recovering from addiction, they shouldn’t take more than 30 milligrams in a single day. According to the CDC’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report, this is the recommended upper limit of the dose.
Overdose Symptoms
Methadone overdose symptoms affect various parts of the body. Overdose on this medication affects the nervous system, lungs, heart, skin and eyes, and digestive system.
These Signs of a Methadone Overdose Include:
- Respiratory problems in the form of shallow and labored breathing
- Drowsiness
- Disorientation
- Fatigue
- Falling into a coma in severe instances
- Muscle twitches
- A weak pulse and low blood pressure
- Vomiting
- Nausea
- Constricted pupils
- Stomach and intestinal spasms
- Bluish tinge in the lips and fingernails
A person experiences life-threatening health effects like labored breathing, low pressure, and falling into a coma that can quickly lead to death.
How Is the Overdose Treated?
Since this medication is an opioid, an overdose can be treated by administering a drug that reverses the breathing difficulties. A study published in the Critical Care journal reveals that buprenorphine is one such drug. It is used because it acts for a more extended period, and there are fewer chances of the patient experiencing withdrawal symptoms.
However, the most commonly used drug to combat an overdose is naloxone (Narcan).
Does Narcan work on Dolophine? Yes, it does because the latter is an opioid. Naloxone acts for a shorter period and is likely to set off withdrawal symptoms. The study further states that they can also use a combination of naloxone and buprenorphine (Suboxone).

To prevent a repeat of the overdose, medical professionals can advise putting a patient on a supervised Dolophine detox regimen. It happens to ensure that they don’t abuse the drug and experience fewer withdrawal symptoms.
Getting Help To Cope With Methadone Side Effects
Although Dolophine has its beneficial medical uses taking this drug can cause side effects, and patients run the risk of overdosing.
Patients need to get help with the side effects of Methadone. This is so that they can continue to benefit from the positives the medication has to offer, like pain management or reducing opioid withdrawal.
Rather than embarking on this coping journey alone, patients should seek professional medical help to deal with the adverse health effects. Expert advice in drug rehab is particularly useful in overcoming addiction and the life-threatening consequences it poses.
Hope Without Commitment
Find the best treatment options. Call our free and confidential helpline
Most private insurances accepted
Page Sources
- U.S. National Library of Medicine, Medline Plus, Methadone. https://medlineplus.gov/druginfo/meds/a682134.html
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Methadone Prescribing and Overdose and the Association with Medicaid Preferred Drug List Policies — United States, 2007–2014. https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/volumes/66/wr/mm6612a2.htm
- Macey, T. A., Weimer, M. B., Grimaldi, E. M., Dobscha, S. K., & Morasco, B. J. (2013). Patterns of care and side effects for patients prescribed methadone for treatment of chronic pain. Journal of opioid management, 9(5), 325. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4001870/
- Eslami-Shahrbabaki, M., Haghdoost, A. A., Mashaiekhi, A., Khalili, N., Amini-Ranjbar, Z., & Ghayomi, A. (2012). Effects of methadone on liver enzymes in patients undergoing methadone maintenance treatment. Addiction & health, 4(3-4), 111. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3905544/
- Hallinan, R., Byrne, A., Agho, K., McMahon, C., Tynan, P., & Attia, J. (2008). Erectile dysfunction in men receiving methadone and buprenorphine maintenance treatment. The journal of sexual medicine, 5(3), 684-692. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18093096/
- Kosten, T. R., & George, T. P. (2002). The neurobiology of opioid dependence: implications for treatment. Science & practice perspectives, 1(1), 13. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2851054/
- Bashore, R. A., Ketchum, J. S., Staisch, K. J., Barrett, C. T., & Zimmermann, E. G. (1981). Heroin addiction and pregnancy. The Western journal of medicine, 134(6), 506–514. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1272838/
- Burns, L., Mattick, R. P., Lim, K., & Wallace, C. (2007). Methadone in pregnancy: treatment retention and neonatal outcomes. Addiction, 102(2), 264-270. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17222281
- U.S. National Library of Medicine, Medline Plus, Methadone Overdose. https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/002679.htm
- Grissinger, M. (2011). Keeping patients safe from methadone overdoses. Pharmacy and Therapeutics, 36(8), 462. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3171821/
- Zamani, N., Buckley, N. A., & Hassanian-Moghaddam, H. (2020). Buprenorphine to reverse respiratory depression from methadone overdose in opioid-dependent patients: a prospective randomized trial. Critical Care, 24(1), 44. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7006192/


