How Long Does Heroin Stay in the System?

Heroin stays in the system for 7.6 to 21.8 minutes because of its short half-life. The liver metabolizes heroin into its metabolites (morphine and 6-MAM) which remains in the system for 24 – 72 hours. Heroin detection time depends on factors like frequency of use, dosage amount, individual metabolism, hydration, body fat, purity, and dose. Heroine is detected in the body systems by detection tests. Samples are taken from urine, blood, saliva, and hair for detection tests. Heroin is detectable in urine for 2 to 5 hours after the use and the remaining traces last for 2 to 3 days. The metabolites remain in the saliva for up to 24-36 hours and more than 3 months in hair. Heroin is detectable in blood for a few hours after the use and traces are left for up to 72 hours, as shown in research titled “How Long Does Heroin Stay in Your System?” published in 2024 by Bicycle Health.
The half-life of heroin is 7.6 to 21.8 minutes which suggests that 50% of heroin is eliminated from the system during this time, according to a research titled “ How Long Heroin Stays in System: Half-Life and Metabolites of Smack,” published in 2024 by Addiction Resource. Heroin detection time is important in medical treatments, recovery processes, relapse prevention, and legal drug testing. Knowing the time and amount of drugs in the body helps in recommending the treatment program and preventing individuals from heroin dependency.
Table Of Contents:
- How is Heroin Processed in the Body?
- How long does Heroin Stay in Your System?
- What tests are done to detect heroin in the body?
- What are the Factors That Influence Heroin Detection Time?
- What is the Half-life of Heroin?
- How Long Heroin’s Metabolites Stay in the System?
- What are the Effects of Heroin?
- What is Heroin?

How is Heroin Processed in the Body?
Heroin is processed in the body through metabolization that transfers heroin into its active metabolites. Heroin crosses the blood-brain barrier within 15-20 seconds and reaches the central nervous system because of its high liquid solubility, according to research titled “Heroin,” published in 2017 by PharmWiki. Heroin converts into the active form called 6-monoacetylmorphine (6-MAM) and then into morphine, after crossing the bloodstream. Heroin stimulates the opioid receptors in the brain and provides feelings of joy, euphoria, pleasure, and pain relief. The liver helps in the metabolism and eliminates the heroin from the system within 30 minutes. The metabolites stay in the body for a long time which increases the feelings of pleasure and pain relief. The sense of happiness and joy encourages individuals to use heroin repeatedly which leads to heroin addiction. The liver breaks down 6-MAM and morphine from the blood and eliminates them from the body through urine.
How long does Heroin Stay in Your System?
Heroin stays in your system for 4 to 90 days, depending on detection methods like urine, blood, hair, and saliva testing. The detection time is influenced by frequency of use, dosage amount, individual metabolism, and body fats.
How long Does Heroin Stay in Urine?
Heroin stays in urine for 2 to 5 hours after the use and the traces stay for almost 2-3 days. Heroine stays in urine for a few minutes, if individuals are not using it regularly. Heroin is detectable for a week in Individuals who are misusing heroin for a long time.
How Long Does Heroin Stay in the Bloodstream?
Heroin stays in the bloodstream for 6 hours after use and its metabolites last up to 72 hours. Heroin stays in the blood for a short time as compared to urine, hair, and saliva. The detection time is short because heroin passes the bloodstream quickly.
How Long Does Heroin Stay in Hair?
Heroin stays in hair for up to 90 days or more depending on the growth and length of hair. Heroin metabolites enter the blood and attach to hair follicles with the help of blood vessels. Hair is used for tracing the record of long-term drug usage.
How Long Does Heroin Stay in Saliva?
Heroin stays in saliva for up to 24 hours after immediate use. Saliva detection is less effective compared to urine because traces are difficult to detect in saliva, according to research titled “How Long Does Heroin Stay in Your System?” published by The Recovery Village Ridgefield.
What tests are done to detect heroin in the body?
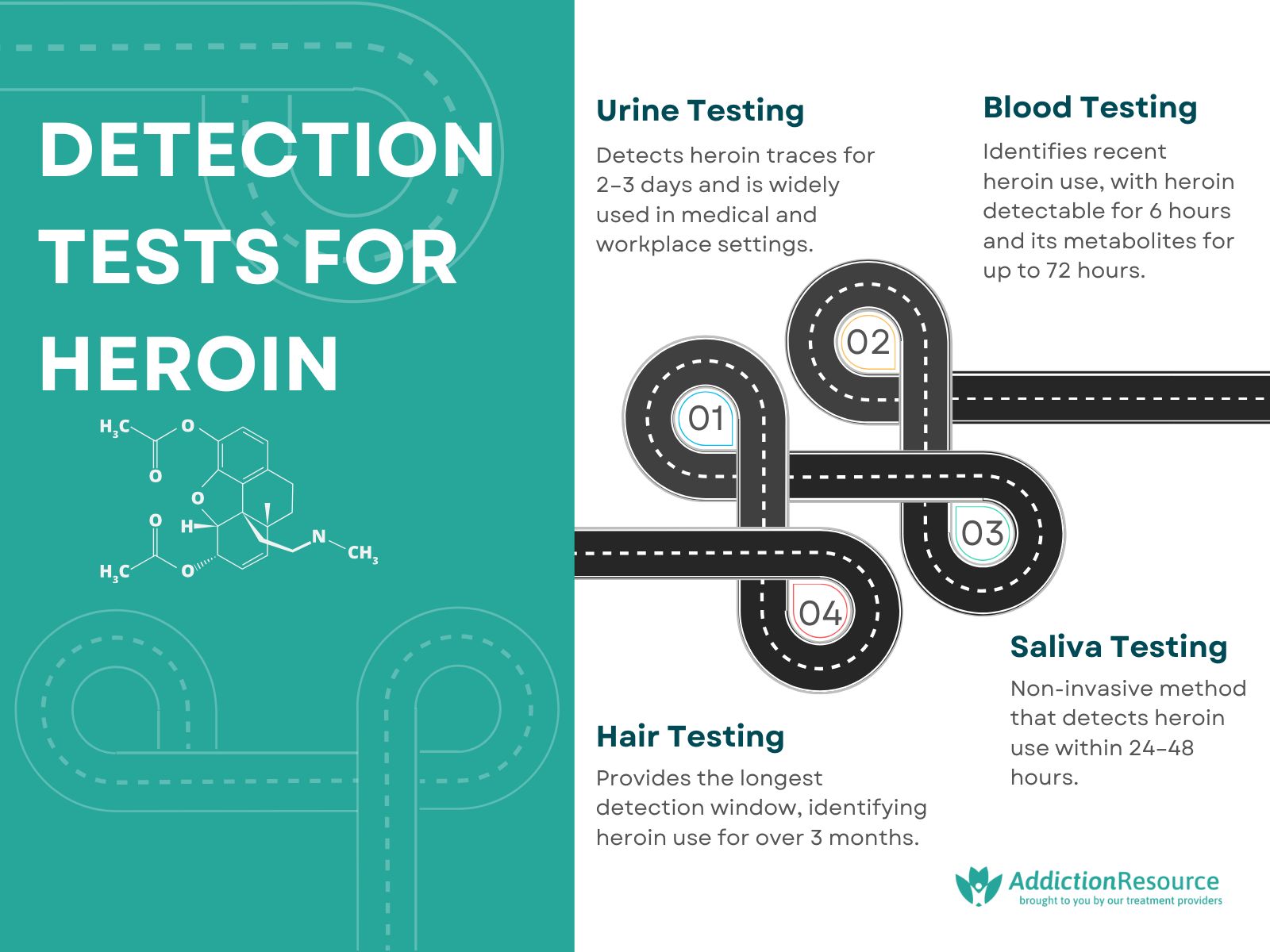
The tests done to detect heroin in the body are urine testing, blood testing, saliva testing, and hair testing.
The 4 detection tests for heroin in the body are listed below:
- Urine testing: Urine screening tests are used in OPTs, workplaces, and medical laboratories. Urine tests are conducted under a doctor’s supervision to achieve accurate results. Heroine traces are detectable in urine for almost 2-3 days, as shown in research titled “How Long Will Traces of Opiate Drugs and Medications Stay in Your Urine?” published in 2023 by Healthline.
- Blood testing: Blood testing is used in legal settings to detect the recent use of drugs through the immunoassay method. Heroin lasts for 6 hours in the blood but its metabolites (6-MAM and morphine) stay in the blood for almost 72 hours which confirms the presence of heroin in the system.
- Hair testing: Hair testing is used mostly in forensics because it provides the longest detection window compared to other tests. The traces are detectable in hairs for 3 months or more. The detection period depends on the growth and length of hair.
- Saliva testing: the detection window for saliva tests is 24 to 48 hours after heroin consumption. Saliva testing is an effective technique for detecting recent heroin use in individuals. Saliva testing is done by collecting a sample from the mouth with the help of an absorbent pad and swab. This technique is easy and is used in the workplace for routine analysis of drug misuse. Heroin was detectable in saliva 2 minutes after the use by both intravenous and smoked routes, according to research titled “Comparison of Heroin and Cocaine Concentrations in Saliva with Concentrations in Blood and Plasma,” published in 1995 by ResearchGate.
What are the Factors That Influence Heroin Detection Time?
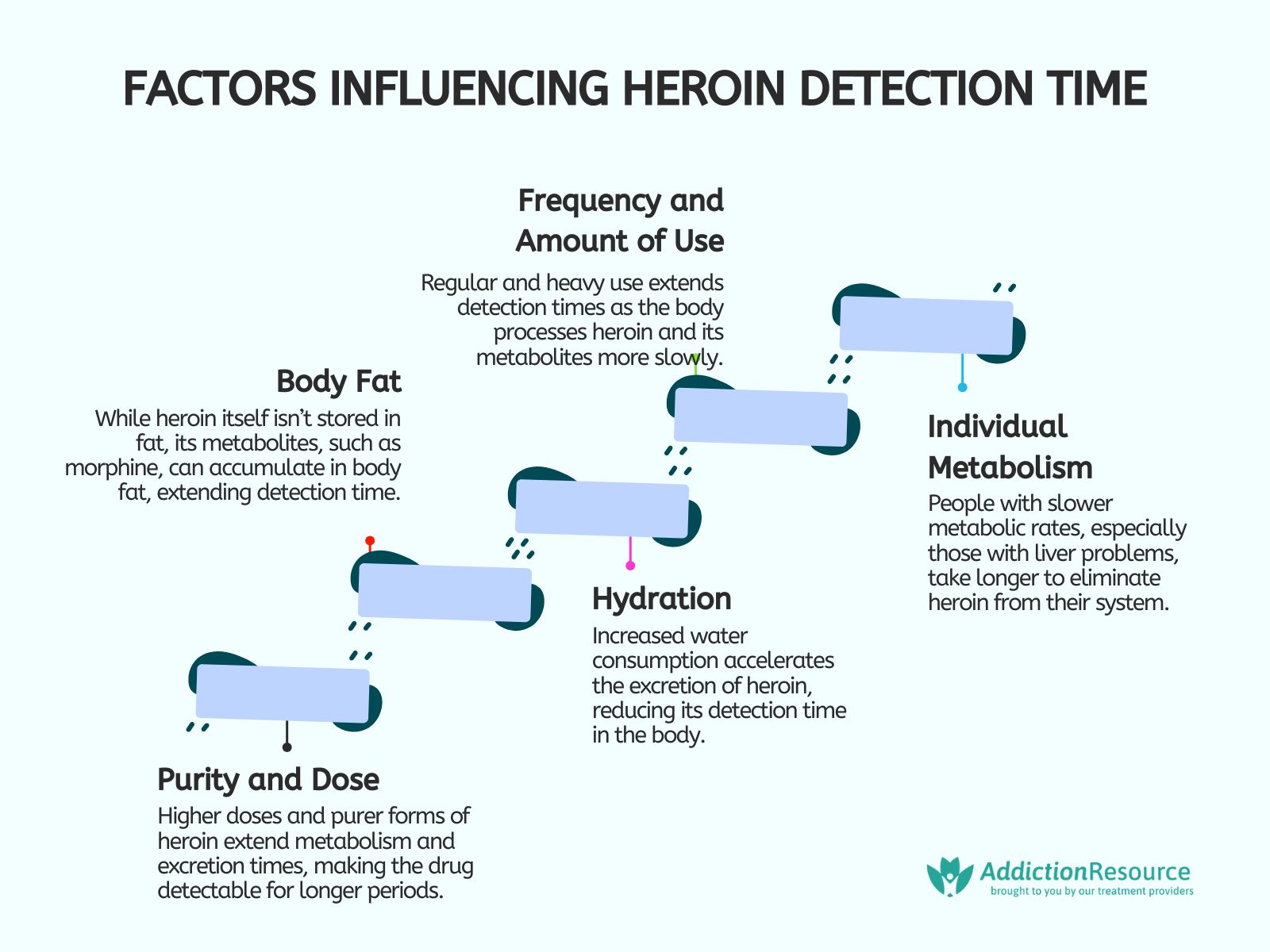
The factors that influence heroin detection time are frequency and amount of use, individual metabolism, purity and dose, hydration, and body fat.
The 5 factors that influence the heroin detection time are listed below:
- Frequency and amount of use: Regular and higher use of heroin increases the detection time in drug tests. The traces of heroin are detectable for a long period in individuals who are using heroin frequently. The metabolism and excretion rate is slow in regular users compared to others.
- Individual metabolism: Individual metabolism affects the detection time of heroin. Clearance time increases in individuals with liver problems because of slow metabolism.
- Body fat: Heroin passes the body stream and is not stored in body fat because of its liquid-soluble nature. The metabolites of heroin, especially morphine, are stored in body fat and increase the detection time, as shown in research titled “Heroin Detection Times – How Long Does Heroin Stay In Your System?” published in 2018 by Opioid Treatment.net.
- Hydration: Doctors keep individuals hydrated to eliminate the side effects of heroin which results in a reduction of the detection time. Heroin clears from the body because of high water consumption.
- Purity and dose: The high purity and dose of heroin increase the detection time because of an increase in metabolism and excretion time. Pure heroin means the presence of an active form of heroin in the body which increases the risk of addiction.
What is the Half-life of Heroin?
The half-life of heroin is 7.6 to 21.8 minutes which means that almost 50% of heroin is eliminated from the system during this time, as shown in research titled “Population pharmacokinetics of heroin and its major metabolites” published in 2006 by PubMed. Heroin has a short half-life, so it is quickly eliminated from the body compared to other opioids like fentanyl, methadone, and cocaine. The remaining heroin metabolizes into its active forms (6-monoacetylmorphine (6-MAM) and morphine) which stays longer in the body.
How Long Heroin’s Metabolites Stay in the System?
Heroin’s metabolites stay in the system for 24 – 72 hours which increases the effects of heroin by increasing the feelings of happiness, joy, and euphoria. The presence of 6-MAM and morphine confirms the misuse of heroin in the system. The detection time of metabolites depends on the drug tests. The metabolites stay in the urine for 24 – 72 hours, for almost 6 hours in blood, for 24-36 hours in saliva, and for up to 90 days in hair. The detection window depends on the factors that influence the time these metabolites stay in the body.
What are the Effects of Heroin?

The effects of heroin overdose are euphoria, drowsiness, shallow or slow breathing, constricted pupils, sudden changes in behavior, disorientation, cycles of hyper-alertness by suddenly nodding off, and droopy appearance.
The 8 effects of heroin are listed below:
- Euphoria: Heroin stimulates the opioid receptors that produce intense feelings of happiness, pleasure, and relaxation and block the pain receptors, as shown in research titled “What are the immediate (short-term) effects of heroin use?” published in 2011 by the National Institute on Drug Abuse. The euphoria effect is short-lived but encourages individuals to use heroin repeatedly which leads to heroin addiction.
- Drowsiness: Individuals feel extremely sleepy and always struggle to stay awake, which impairs their ability to perform normal tasks. Heroin affects the normal activities of the central nervous system and causes unconsciousness or drowsiness.
- Shallow or Slow Breathing: Heroin addiction leads to oxygen deprivation that weakens or entirely stops breathing. Slow breathing causes respiratory failure and even leads to death, according to research titled “Heroin and its metabolites: relevance to heroin use disorder,” published in 2023 by the National Library of Medicine.
- Constricted Pupils: Constricted pupils are the physical side effect of heroin addiction that causes pupils to shorten, even in low-light conditions. Heroin enters the brain and damages the parasympathetic system which leads to constriction of pupils.
- Sudden Changes in Behavior or Actions: Individuals show unpredictable actions, such as aggression, social withdrawal, and confusion. These changes are alarming and lead to heroin misuse.
- Disorientation: Heroin impairs cognitive functions, causing confusion and difficulties in focusing. Individuals seem lost or unable to recognize their surroundings.
- Cycles of Hyper-Alertness and Nodding Off: Heroin affects the functioning of the CNS and alters their mood. The feeling of happiness immediately increases after the consumption but causes extreme changes in moods when the effects wear off which leads to irritability and nodding.
- Droopy Appearance: Individuals experience changes in facial muscles, facial expression, and drooping eyelids because of a heroin overdose. A droopy appearance makes individuals look more tired and dull.
What is Heroin?
Heroin is an illicit opioid that is produced from morphine and extracted from the opium poppy plant, according to research titled “Heroin” published by the United States Drug Enforcement Administration. Heroin comes in brown powder, white powder, and sticky black tar that is injected, snorted, and smoked. Heroin stimulates the mu-opioid receptors that enhance the feelings of euphoria, and reduce pain which encourages individuals to use it repeatedly. Heroin is a Schedule-I drug which means that the chances of heroin dependency are high.
What Are the Dangers of Heroin Addiction?
The dangers of heroin addiction are respiratory depression, liver damage, kidney failure, severe dependence, anxiety, depression, and neglecting daily tasks. Long-term heroin affects social life and job opportunities, which lowers the quality of life. Individuals using heroin for chronic pain are at risk of heroin addiction which leads to death. Around 9,173 individuals died in 2021 because of heroin overdose, as shown in research titled “Heroin,” published by the National Institute on Drug Abuse.
Does Heroin Show Up on a Drug Test?
Yes, heroin shows up on drug tests like urine, saliva, blood, and hair tests. Drug screening tests detect heroin through its metabolites that are present in the system for a longer time than heroin. The detection windows depend on the type of drug tests. Hair and urine tests have a longer detection window compared to saliva and blood tests. Heroin is eliminated from the body within 30 minutes but its metabolites stay for 24-72 hours which confirms the heroin in the system.
Do Heroin and Fentanyl Have the Same Detection Times?
No, heroin and fentanyl do not have the same detection times. Heroin metabolizes quickly because of its short half-life but fentanyl stays longer in the body for almost 35 hours. Fentanyl is 50 to 100 times stronger than heroin and its metabolites, which increases the detection window of fentanyl. Drug tests have more detection time for fentanyl compared to heroin.
Does Heroin Stay in the System Longer Than Other Opioids?
No, heroin does not stay in the system longer than other opioids like methadone, buprenorphine, and fentanyl. Heroin has a short half-life of 7.6 to 21.8 minutes and is quickly metabolized into 6-monoacetylmorphine (6-MAM) and morphine, which are excreted within 1-3 days through urine. Opioids like methadone, fentanyl, and buprenorphine have longer half-lives, allowing them to remain detectable for several days or even weeks. The elimination speed of heroin contributes to its intense but short-lasting effects, making the detection window shorter than other long-acting opioids.
Can Heroin Be Detected After a Week?
No, heroin is not detected after a week because of its short half-life and quick metabolization. Heroin is metabolized within 7 to 21 minutes, but its metabolites such as 6-monoacetylmorphine (6-MAM) and morphine are detectable in urine for up to 3 days. Blood tests identify heroin for about 6 hours, and saliva tests for up to 24 hours. However, hair tests provide a longer detection window, showing heroin use for up to 90 days.
What Is the Elimination Process for Heroin?
The elimination process for heroin is metabolism and excretion. Heroin undergoes rapid metabolism after entering the body, converting first into 6-monoacetylmorphine (6-MAM) and then into morphine. The metabolization happens in the liver after which heroin is excreted through urine. The elimination half-life of heroin is 7.6 and 21.8 minutes, but its metabolites can stay longer for up to 3 days in the system.
What Is Heroin Withdrawal and Detox?
Heroin withdrawal and detox are the symptoms and treatment plans for individuals with a heroin dependency. Withdrawal symptoms are physical and psychological that occur when individuals reduce or stop using heroin after long-term use. Withdrawal symptoms include anxiety, restlessness, muscle pain, nausea, sweating, and severe cravings. Withdrawal symptoms make it problematic for individuals to quit heroin. Detox is typically the first step in a treatment plan under a doctor’s supervision. Detoxification is the removal of heroin from the body through medications such as methadone or buprenorphine to manage withdrawal symptoms.
Hope Without Commitment
Find the best treatment options. Call our free and confidential helpline
Most private insurances accepted




