
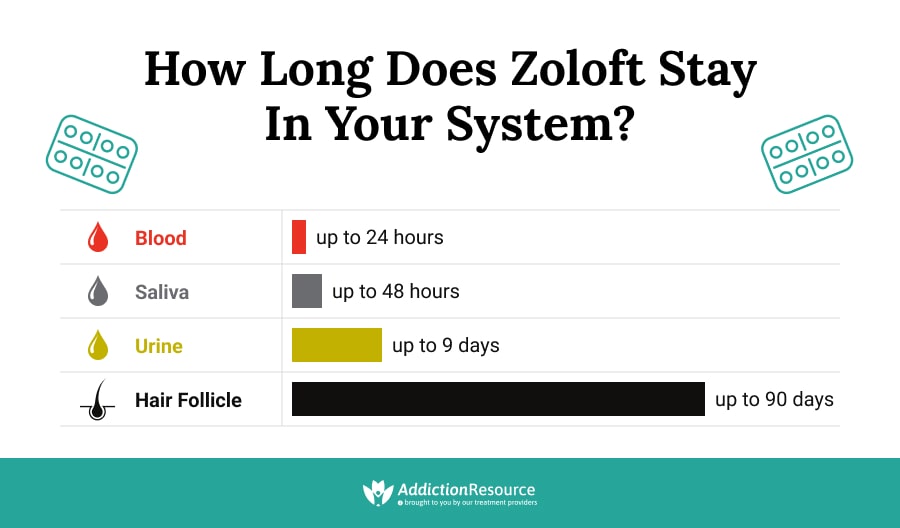
Zoloft stays in your system for approximately five days, with about 99% of sertraline eliminated during this period. The drug appears in urine tests for up to 9 days and remains detectable in hair samples for weeks or months after stopping.
The mechanism of action of Zoloft involves selectively inhibiting the neuronal uptake of serotonin in the central nervous system. This inhibition increases synaptic serotonin concentration, leading to functional changes associated with enhanced serotonergic neurotransmission.
The half-life of Zoloft averages 26 hours according to clinical data. Individual factors like age, sex, body mass, and liver function affect elimination time, with younger males typically metabolizing the drug faster than females in the same age group.
Table Of Contents:
Typically, patients that have specific social disorders and are recommended to use sertraline don’t really know the mechanism of action of Zoloft. However, familiarizing oneself with how the drug works are significant, because it helps one to understand prescriptions better and know precisely how each dose potentially affects the body.
Additionally, anybody planning to stop taking anti depression and anxiety medicine must know the possible symptoms that withdrawal may trigger. To successfully get rid of sertraline, one must know the half-life time, factors tat may affect the time of staying and how long does Zoloft stay in your system after stopping.
How Long Does It Take For Zoloft To Work?
The medication works by slowing down the reabsorption of serotonin in the brain. Serotonin is a chemical neurotransmitter that transmits electrical pulses from one neuron to the other in the brain. It is a “mood stabilizer” because the levels of serotonin in the body directly impact the mood of each person. Low levels translate into bad moods/mood disorders, and high levels translate into high spirits.
Normally, serotonin is instantly re-absorbed, but Zoloft drug delays this re-absorption for a reasonably long period. This delayed re-absorption allows it to send additional messages to the receiving neuron, boosting the mood of the patient.

Zoloft Mechanism of Action in the Body
The exact sertraline mechanism of action is not fully known, but the drug is known to selectively inhibit the CNS neuronal uptake of serotonin. The result of this is an increase in the synaptic concentration of serotonin in the Central Nervous System (CNS), which gives way to many functional changes associated with intensified serotonergic neurotransmission.
It is perceived that these tamperings are responsible for the effects of the drug during long-term administration.
Pharmacodynamics
Sertraline has one active metabolite. It is also less sedative, anticholinergic, and has fewer cardiovascular effects when compared to tricyclic antidepressants. This is because the medication does not have antihistamine, clinically important anticholinergic, or adrenergic (alpha1, alpha2, beta) blocking activity.
Sertraline also has no significant relationship with GABA, dopaminergic, benzodiazepine receptors, or serotonergic (5HT1A, 5HT1B, 5HT2) receptors in vitro. It exhibits weak inhibitory actions on the neuronal uptake of dopamine and shows no inhibitory activity on monoamine oxidase.
In a study published on the NCBI web site, the chronic administration of sertraline down-regulates membrane norepinephrine receptors.
This can also be observed with other antidepressants useful in the treatment of a Major Depressive Disorder. However, the expected pharmacological action of sigma receptors in the Zoloft mechanism of action is unclear.
Half-Life And Pharmacokinetics
In the human body, following oral once-daily medication over the range of 50 mg to 200 mg for two weeks, the peak plasma half-life occurred between 4.5 – 8.4 hours after administration. Based on the information provided by Pfizer, the average terminal sertraline half-life is about 26 hours. Steady-state concentrations are reached after a week of once-daily administration, and roughly two-fold accumulation up to steady-state concentration is perceived.
The single-dose bioavailability of the pill is accurately equal to an equivalent medication of the oral solution.

However, the effects of food on the bioavailability of oral pills and concentrations were studied in subjects delivered a single dose with and without food. For the tablet, the AUC (plasma concentration-time curve) was slightly increased when Zoloft was taken with food, but the Cmax was 25% greater. Meanwhile, the Tmax (Time is taken to reach peak plasma concentration) decreased from 8 hours after administration to 5.5 hours. For the oral concentrate, the Tmax was slightly extended from 5.9 hours to 7 hours.
Protein Binding
FDA’s study on protein binding points out that this antidepressant is highly bound to proteins (98%) in the range of 20 to 500 ng/ml, mostly to albumin and 1-acid glycoprotein. This was performed with radiolabeled H-sertraline; however, between 300 and 200 ng/ml respectfully, sertraline and N-desmethyl sertraline did not change the plasma protein binding of two other highly protein-bound drugs like warfarin and propranolol.
How Long Can Zoloft Be Detectable on the Drug Test?
Zoloft can yield a false-positive result in a drug test. The possibility of a false-positive test ranges from 5 to 10%. The possibility for a false-negative test falls within 10 to 15%.
These drug tests can be done with blood, urine, saliva, or even hair samples. The type of lab tests that will be run, as well as the timing of the drug test and the specimen used, will influence the results.
For anyone scheduled to undergo a drug test, here are the top facts about Zoloft and drug tests that should be known:
How Long Does Zoloft Stay in Blood?
It takes approximately five days to eliminate about 99% of sertraline from the system. Using saliva, hair, and fingernail samples for drug testing are unusual and not routine. An interplay of many factors concerning individual conditions may affect how long Zoloft stays in the body. How long it stays detectable in the blood depends on the amount consumed right before withdrawal and the sertraline half-life.
How Long Does Zoloft Stay in the Urine?
In a study of radiolabeled sertraline requiring two healthy male subjects, the total radioactivity of about 40-45% of sertraline components in urine was observed up to 9 days after taking the medication with a negligible amount of <0.2% detected in the unchanged parent compound. In the same period, the total radioactivity accounted in feces was from 40-45%, where 12-14% of the radioactivity was unaltered sertraline.
How Long Does Zoloft Stay in the Hair?
Zoloft stays in hair samples longer than any other sample. The elimination period can last for weeks or months, even when the person has completely stopped feeling the effects of the drug in the system. This increases the chances of a positive result on a Zoloft drug test a long time after stopping the medication.
How Long Does Zoloft Stay in the Saliva?
Zoloft is typically wholly eliminated from saliva samples within a few days. This means that when one stops using the drug, it can still show up in drug tests at least 48 hours after stopping.
How Is Zoloft Stored In The Body?
Metabolism
How is Zoloft metabolized? This drug is broadly metabolized in the liver. Its metabolism includes N-demethylation, Oxidative deamination, N-hydroxylation, and glucuronidation of sertraline carbamic acid.
Zoloft undergoes N-demethylation to give way to the formation of N-desmethyl sertraline. This retains significantly less pharmacological activity than the initial compound. The metabolic pathway is mainly catalyzed by cytochrome P450 CYP2B6, with CYP3A4, CYP2C19, and CYP2D6 contributing to a minor extent.
Both N-desmethyl sertraline and sertraline undergo oxidative deamination and subsequent reduction, hydroxylation, and glucuronide conjugation. Zoloft also is known for making weight changes in the body.
Following intake of the pill and the introduction of sertraline into the body, the following pathway occurs:
- Sertraline is absorbed by the body more rapidly when taken with food and more slowly without. Peak plasma concentration happens at about 4 to 6 hours after taking in a pill. This information is important to avoid sertraline overdose.
- The drug concentration begins to be cut into half by about 24 up to 26 hours following intake, broken down by enzymes of the liver. Approximately 45% of sertraline will be excreted through the kidneys and the rest through feces.
- By Day 5 following pill intake, about 99% will have been excreted from the body. However, desmethyl sertraline will take longer to exit the system. Once again, individual differences will influence how long it takes to rid one’s system of the drug’s traces.

Elimination
The average elimination time of plasma sertraline is 26 hours. This translates into the fact that steady-state sertraline plasma levels can be achieved with approximately seven days dosage of once-daily on the drug. However, the real case-by-case figures may vary according to a number of factors.
Factors That Influence How Long for Zoloft to Leave System
The elimination period of sertraline depends on several factors. These factors affect the length of time it takes to clear the drug from the system:
Dosage
The first consideration in determining how long does Zoloft stay in your system after one stops taking it is by noting the dosage prescribed for a patient. It matters whether the patient is taking 25 mg or 200 mg of Zoloft. This indicates the concentration levels of sertraline in the system.
The higher dose one takes, the longer it takes for the medication to completely breakdown and, eventually, be wholly excreted from the body. The frequency of drug intake per day also determines the level of sertraline concentration inside the body. The length of time that one has been medicating with the antidepressant, will also affect how long it can stay in the system.
Age and Sex
In general, younger males break down the drug and its metabolite, Desmethylsertraline, at a faster rate than females within the same age group. A particular study published on NCBI was able to establish this comparison between young adult males and females between the ages of 18 to 45. The study found that the average time it takes for young adult females to breakdown the sertraline and Desmethylsertraline was similar to the rate at which these were broken down by older males and females also included in the study.
Body Mass
The person who has a more immense body mass will eliminate the drug much slower than the person with a low body mass. Half-life will depend on the patient’s weight as well. The higher the presence of fats, the more likely that more of the drug has been stored in human fats and, therefore, the longer it will take to break it down. Also, Zoloft causes weight gain or loss in some patients during the treatment course.

Heredity
According to this study, liver health can be a major driver of how long Zoloft can stay in your system. The liver controls and regulates the enzymes that help breakdown food and drugs inside the gut. Some people have inherited enzymes that can directly cut down Zoloft half-life, whereas the ones who do not have such enzymes will take longer to break down its active compounds. Health conditions, in general, can affect the rate of metabolism.
Taking Zoloft With Food
This drug may or may not be taken with a meal. Those who take it with a big meal get to absorb more of the sertraline faster, whereas taking the drug without food may cause it to stay in the system longer. Liver functioning also plays part in sertraline elimination time. It is recommended to avoid all kinds of alcohol with Zoloft.
Zoloft Interactions With Other Drugs
There are certain medications that affect the level of enzymes that the body uses to metabolize Zoloft. Some of these improve enzyme production while others inhibit the production of the same. When sertraline is taken with medications that drive up the production of these enzymes, the body is able to metabolize the drug faster.
On the contrary, medicines that inhibit the production of these enzymes cause Zoloft to become metabolized more slowly.
Summarily, the half-life and elimination period of Zoloft in the human system is not the same figure in every situation. One first needs to identify the type of test that needs to be done – urine and blood tests may show different results, for instance – and one also needs to take into account the other factors discussed above. However, in most cases, the drug will typically be clear of the system by the end of the tenth day.
Page Sources
- Hardeep K. Singh, Abdolreza Saadabadi. Sertraline, 2020, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK547689/
- Zaorui Zhao, Han-Ting Zhang, Elianna Bootzin, Mark J Millan, and James M O’Donnell, Association of Changes in Norepinephrine and Serotonin Transporter Expression with the Long-Term Behavioral Effects of Antidepressant Drugs, 2009, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2727703/
- The U.S. Food and Drug Administration, Zoloft, 2008, https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2009/019839s070,020990s032lbl.pdf
- National Library of Medicine: National Center for Biotechnology Information, 2020, https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Sertraline
- R A Ronfeld, L M Tremaine, K D Wilner, Pharmacokinetics of sertraline and its N-demethyl metabolite in elderly and young male and female volunteers, 1997, https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9068932/
- JEAN-LOUIS DE´ MOLIS, PASCAL ANGEBAUD, JEAN-DIDIER GRANGE, PETER COATES, CHRISTIAN FUNCK-BRENTANO1 & PATRICE JAILLON, Influence of liver cirrhosis on sertraline pharmacokinetics, 1996, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2042671/pdf/bcp_0428.pdf
- Sannidhya Varma, Himanshu Sareen, J.K. Trivedi, The Geriatric Population and Psychiatric Medication, 2010 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3031932/
- J H Wang, Z Q Liu, W Wang, X P Chen, Y Shu, N He, H H Zhou, Pharmacokinetics of sertraline in relation to genetic polymorphism of CYP2C19, 2001, https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11452243/

 Reviewed by:
Reviewed by:  Written by:
Written by: 
 FindTreatment.gov
FindTreatment.gov