
As the “web” evolved into the most accessible tool available, reaching 94% accessibility among Americans, internet addiction (IA) has emerged as a potential problem, particularly among young people. This addiction may cause a decline in work and school performance, strained interpersonal relationships, as well as cause anxiety and depression.
Read on to learn about this addiction, its causes and medical manifestations, and how to get help for this emerging disorder.
Table Of Contents:
What is Internet Addiction (IA)?
Addiction to the internet is an impulse control disorder characterized by a lack of control over internet use, with people exhibiting excessive use of digital media such as social networking and streaming platforms (Netflix, Disney+, Prime Video), music apps (Spotify, YouTube and TikTok music), online shopping or gaming, etc.
As Generation Z has grown up with easy access to technology, their dependence on the Internet for communication, entertainment, and education has significantly increased.
In the U.S., teenagers spend 7 hours and 22 minutes daily using digital media outside school assignments, more time than they usually sleep or attend classes. This figure is a source of concern, considering that American adults spend an average of 8 hours and 34 minutes daily, including time at work or using work apps. Teenagers are spending unhealthy amounts of time online.
Types of Addiction to the Internet
Studies have concluded that this addiction is not heterogeneous, and users tend to get addicted to different activities on the internet, such as:
- Social media addiction: Excessive use of social networking platforms
- Online gaming addiction: Obsessive playing of online video games
- Cybersex addiction: May include masturbation and pornography addiction, engagement in online sex
- Online shopping addiction: Excessive and compulsive purchasing of goods and services online
- Information overload addiction: Constantly consuming online information (podcasts, blogs)
- Compulsive web surfing: Endless browsing of websites, forums, or content without a specific purpose
Why is the Internet Addictive?
As the Internet constantly expands its range of services and scope, its use is on an exponential rise, resulting in users spending more time engaged online. It is predicted that by the end of 2024, individuals will have spent 508 minutes (8 hours and 46 minutes) online, which is almost an hour more than in 2020.
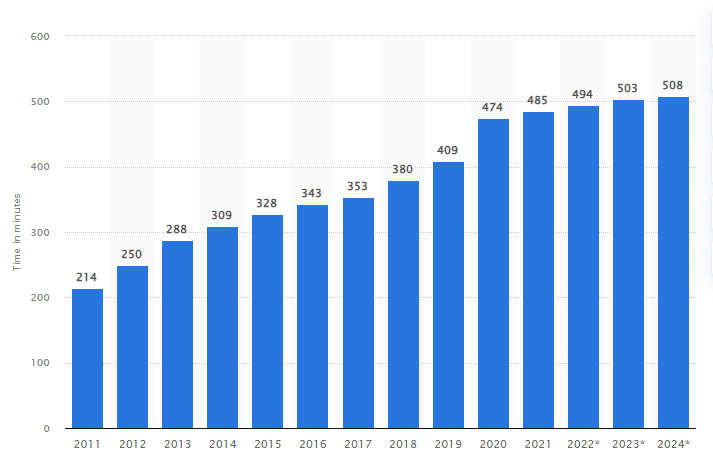
Average time spent per day (in minutes) with digital media in the United States from 2011 to 2024 (Source: Statista.com)
This prediction shows the highly addictive nature of the Internet due to the following reasons:
- Easy access to smartphones, tablets and computers
- Pressure from peers to engage in online activities
- Using the internet to cope with stress and anxiety
- Limited parental oversight on children and teenagers’ online activities
- Exploring online content and gaming out of curiosity or social validation
- Vulnerability due to mental health issues like ADHD, depression, social anxiety or addiction predisposition
- Seeking social validation and connection through online interactions
- Wide variety of online content
Internet Addiction among Children, Teens and Young Adults
Since during adolescence, the brain’s reward system of children, teens and young adults is still under development, they are more susceptible to internet and social media addiction.
Around ages 10 to 12, the brain becomes highly sensitive to social rewards due to increased receptors for happiness hormones like oxytocin and dopamine in the ventral striatum. Social media like TikTok and Instagram trigger a dopamine and oxytocin rush with likes, comments and shares, activating the brain’s reward system.
Children, teens and young adults, particularly those lacking a stable self-concept and emotional regulation, may feel compelled to scroll and post to feel socially validated. This behavior pattern is clinically important since problematic social media use is linked to depression and self-esteem issues in children and teens.
Signs and Symptoms of Internet Addiction
Since this addiction has yet to be included in diagnostic manuals, research recommends following the following symptom criteria:
- Constantly thinking about getting online
- Spending excessive amounts of time online to achieve satisfaction
- Repeated, unsuccessful attempts to control or reduce internet use
- Restlessness, mood swings or depression when attempting to cut down on the use
- Spending more time online than initially intended
- Endangering relationships, job prospects or educational opportunities due to Internet use
- Lying about Internet habit use
- Using the Internet to ignore or ease negative emotions
- Feeling defensive or guilty about Internet use
- Experiencing a sense of euphoria while engaging in online activities
Physical symptoms of addiction to the internet may include carpal tunnel syndrome, eye strain, headaches, sleep disturbances and significant weight changes.
Internet Addiction Self-Help and Treatment
Implementing new healthy habits is the first action to approach this addiction. Self-help tips may include:
- Establish limits on your internet use, such as designated screen-free times
- Turn off notifications from social media or other apps
- Limit internet use to one device
- Prioritize in-person activities and meetings
- Daily track your online activities and how much time you spend online
- Identify offline activities or hobbies that you enjoy and make time for them
- Engage in mindfulness meditation to identify your internet usage patterns and triggers
- Seek support and assistance from family and friends
Treatment Options
If, after implementing self-help strategies, your addiction persists or worsens, consider seeking a therapist and discussing the following treatment alternatives:
Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) is often the first option for treating internet addiction due to its effectiveness in addressing similar addictions, such as gambling disorder, compulsive shopping, bulimia nervosa and binge eating disorders.
CBT focuses on identifying and changing unhealthy thought patterns and behaviors, providing individuals with practical strategies to manage their internet use and develop healthier habits.
Other Behavioral Interventions
Behavioral interventions involve identifying triggers, building intrinsic motivation and learning alternative behaviors. Patients engage in real-life social activities, receive psycho-education and undergo exposure therapy to manage cravings.
Medication
Although no medications are approved for internet addiction, in cases where underlying mental health conditions contribute to addictive behaviors, medications like antidepressants may be prescribed to manage symptoms of depression or anxiety.
Other medications like mood stabilizers or antipsychotics may be considered for co-occurring mood disorders or psychotic symptoms.
Support Groups
Support groups offer a platform for individuals to connect, share experiences, and receive support for addictions. Local support groups, led by professionals, provide face-to-face interaction and structured assistance. Engaging in both types of groups enhances recovery efforts and offers long-term support.
Internet Addiction – Final Considerations
In the past decade, the internet has become such an indispensable tool in our lives that the goal of completely disconnecting from it is unrealistic.
However, self-regulation, especially for children and teenagers, can prevent emotional dependency on it. When the addiction is already present, an integrated treatment plan addressing all aspects of the situation is necessary, with family therapy proving beneficial for children and teenagers.
If, after reading this article, you suspect an addiction to the internet, seek professional help for better recovery outcomes.
People Also Ask
What is internet addiction?
Addiction to the internet is a compulsive behavior involving excessive, prolonged internet use, leading to negative consequences such as significant impairments in both physical and mental health along with a decline in social, academic and work performance.
How do I find internet addiction treatment near me?
To find internet addiction treatment nearby, search online directories, ask for referrals from healthcare professionals or trusted individuals, and contact local mental health organizations or universities. Additionally, consider exploring online resources and teletherapy services if local options are limited.
Why is the internet so addicting?
The internet offers endless entertainment, instant gratification, social interaction and access to information, triggering dopamine release in the brain. Its convenience and variety can lead to addictive behaviors, especially when combined with factors like isolation or stress.
How internet addiction affects the brain?
Addiction to the internet can alter brain structure and function, affecting areas involved in decision-making, impulse control and reward processing. Excessive use may lead to changes in dopamine levels, similar to those seen in substance addiction.
Hope Without Commitment
Find the best treatment options. Call our free and confidential helpline
Most private insurances accepted
Find Drug Rehabilitation Centers Near You Anywhere In the US
Addiction Resource team has compiled an extensive list of the top drug rehabilitation facilities around the country. Use our locator tool to find the best centers near you.
Page Sources
- Topic: Internet usage in the United States. (2024, March 13). Statista. https://www.statista.com/topics/2237/internet-usage-in-the-united-states/
- Diotaiuti, P., Mancone, S., Corrado, S., De Risio, A., Cavicchiolo, E., Girelli, L., & Chirico, A. (2022). Internet addiction in young adults: The role of impulsivity and codependency. Frontiers in Psychiatry, 13. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2022.893861
- Lozano-Blasco, R., Robres, A. Q., & Sánchez, A. S. (2022). Internet addiction in young adults: A meta-analysis and systematic review. Computers in Human Behavior, 130, 107201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2022.107201
- Bickham, D. S. (2021). Current Research and Viewpoints on Internet Addiction in Adolescents. Current Pediatrics Reports, 9(1), 1-10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40124-020-00236-3
- Kumar, M., & Mondal, A. (2018). A study on Internet addiction and its relation to psychopathology and self-esteem among college students. Industrial Psychiatry Journal, 27(1), 61-66. https://doi.org/10.4103/ipj.ipj_61_17
- Time spent with digital media in the U.S. 2024 | Statista. (2023, August 29). Statista. https://www.statista.com/statistics/262340/daily-time-spent-with-digital-media-according-to-us-consumers/
- Cash, H., Rae, C. D., Steel, A. H., & Winkler, A. (2012). Internet Addiction: A Brief Summary of Research and Practice. Current Psychiatry Reviews, 8(4), 292-298. https://doi.org/10.2174/157340012803520513
- Abrams, Z. (2023, August 3). Why young brains are especially vulnerable to social media. https://www.apa.org/news/apa/2022/social-media-children-teens
- Hendrikse, C., & Limniou, M. (2024). The use of Instagram and TikTok in relation to problematic use and Well-Being. Journal of Technology in Behavioral Science. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41347-024-00399-6

 Reviewed by:
Reviewed by:  Written by:
Written by: 
 FindTreatment.gov
FindTreatment.gov