Lysergic acid diethylamide, also known as acid, is perhaps the best-known hallucinogenic drug. It has been used since the early 1900s. Despite situational reductions in its illegal production, the drug has found its popularity increasing once again in these modern times.
This relatively rampant use, particularly among younger people, prevents the opportunity for serious LSD side effects to develop. Some of these can occur in the short-term, while others result from long-standing damage to the body and brain.
Table Of Contents:
This article will discuss the side issues of Lysergic acid diethylamide that can occur in addicts and how it acts in an addict’s brain and its risks towards pregnancy.
Short Term Effects of Acid Abuse
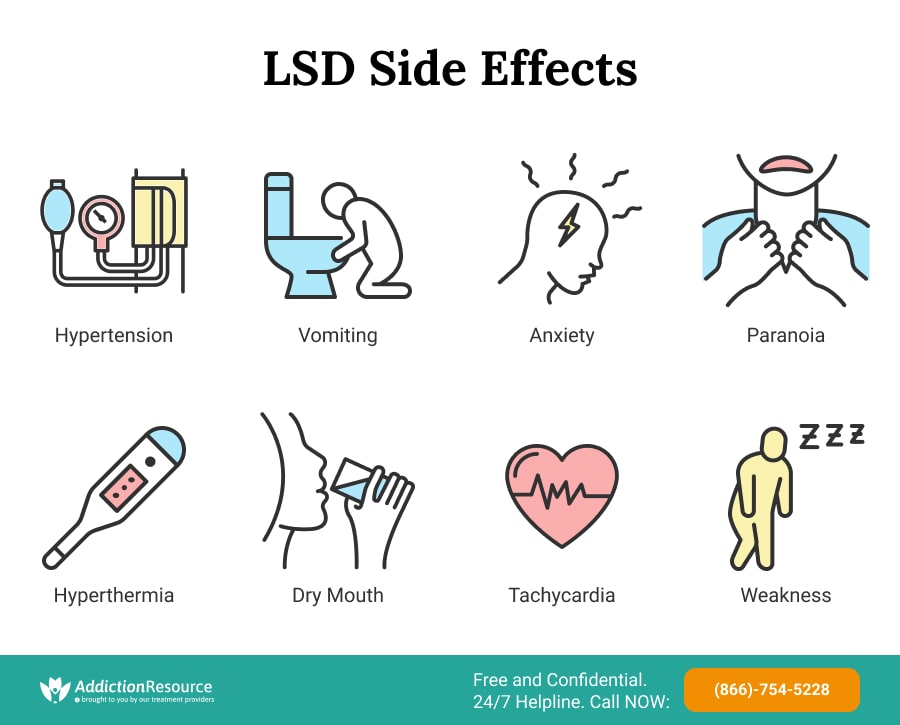
While acid addicts use the drug for the altered perception and hallucinations it gives them, many undesired LSD side effects come with its use in the short-term.
These Include the Following:
- Increased blood pressure (hypertension)
- Increased body temperature (hyperthermia)
- Increased heart rate (tachycardia)
- Anxiety
- Paranoia
- Confusion
- Rapid changes in emotions
- Loss of appetite
- Headaches
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Sweating
- Dry mouth
- Weakness
- Sleeplessness
- Impulsivity
- Increased suggestibility
Long Term Effects of LSD Abuse
For individuals who use this substance persistently, there can begin to be some long term effects of LSD, particularly on the brain. In some cases, even abstaining from it or reducing intake can do little to reverse the damage caused.
Even with microdosing, these side effects of LSD can present. This is why it is important to get help for an acid addiction as soon as possible. The following are some of the long term effects of LSD:
- Hallucinogen Persisting Perception Disorder (HPPD): This condition can affect addicts for years even after their last dose of acid. HPPD is a condition that has an individual experience flashbacks of visual hallucinations that were had during a previous trip. For an addict who has been abstinent for years, this can be distressing. They may suddenly notice distortions in their vision, such as objects appearing blurry, colors being intensified, or what seems to be static overlapping their vision (visual snow). Some individuals may merely have brief flashbacks, while others have persistent visual changes. Further use of hallucinogens will worsen the condition. This condition is rare, and there is no definitive treatment for it, though medication like clonazepam and SSRIs are said to help in some cases.
- Persistent psychosis: This is a condition whereby an individual experiences disturbances in their perception of sensory stimuli such as lights and sounds, paired with paranoia, mood changes, and irrational behavior.
- Depression: This can occur due to the changes that acid causes in the central nervous system’s reward pathways.
- Persisting changes in neurochemistry: Consistent abuse of lysergic acid diethylamide shows alterations in neurochemistry that are long-standing.
- Flashbacks: These are similar to what is experienced in individuals with HPPD. However, these tend to be milder than in HPPD and are sometimes said to be pleasant.
How Does Acid Affect The Brain?
As a drug that derives its action solely from acting on the brain, LSD effects on brain physiology can be significant. These LSD side effects are manifest in different ways. It is important to understand its mode of action to understand its reactions.
As acid’s acute effects begin to fade, the addict may be met with feelings of anxiety or depression. With persistent use, these symptoms can become long-term concerns.
PNAS study used advanced neuroimaging processes and was able to observe the activity of the brain under the influence of acid. There was increased blood flow to the visual cortex, which related to the production of visual hallucinations by the drug. It was found that more areas of the brain were contributing to visual information, even when the eyes were closed.
It also binds to specific serotonin receptors known as 5-HT2A receptors. When it does this, it can produce symptoms that are similar to those that patients with schizophrenia have. It also has some effect on dopamine receptors and glutamate, but less so than serotonin.
Apart from producing schizophrenic symptoms, the targeting of serotonin receptors can affect an array of normal bodily functions regulated by the neurotransmitter.
LSD effects on brain chemistry can affect functions such as:
- Mood
- Sensory perception
- Sleep
- Hunger and appetite
- Sexual behavior
- Body temperature
- Intestinal muscle control
Due to its targeting of glutamate as well, it can affect some of these bodily functions:
- Perception of pain
- Emotion
- Learning and memory
- Responses to the environment
What Is Dangerous About Lsd Tolerance?
Tolerance developing in an addict is dangerous, as it pushes them to take higher doses of the drug to feel their familiar reactions. These higher doses can push into toxic ranges that have lasting effects on the body.

With the bodily functions that acid can affect the brain of an addict, the damage can be serious when the doses taken are very high. This can result in mental problems and impairment of many mental functions.
At a point, an addict may be fed up with continually increasing their dosage. This may result in them transitioning to drugs, which have a greater effect on them and carry much more danger and the risk of addiction than the likelihood of an LSD overdose. Many abusers of acid combine it with other drugs such as speed or alcohol.
People take higher doses with tolerance also leads to more unpredictable behavior.
This greatly increases the risk of causing injury to themselves and others, and even death. A 2018 study also found evidence that one of LSD’s long-term issues is long-lasting personality changes, even following one-time use of a hallucinogenic substance. This shows how significant of an effect high doses can have.
The Effects of Acid on Pregnancy
Similar to other drugs, there are dangers involved in the use of acid during pregnancy. In animal studies, it was found to build up in the placenta and bind to receptors there. Another animal study showed an increased chance of spontaneous abortion early in pregnancy when exposed to the drug.
In human cases, some babies of mothers who abused the drug were born with eye abnormalities such as cataracts and abnormally small eyes. These cases show a significant risk in the use of acid by pregnant mothers.
The Side Effects of Microdosing
Apart from simply having a trip, many acid addicts microdose with the drug. This is the act of taking small doses to increase mental ability in different domains. Even in microdoses, it can pose a danger to health. Many LSD tests were done to find out about the dangers of microdosing, but one study interviewed people who took microdosing. Though the study was not specific to the effects, about 10% of the respondents stopped microdosing due to negative experiences. Most of these were said to be of a psychological nature.
Microdosing can also cause the development of tolerance, which can develop into the abuse of the drug.
The side effects of LSD are numerous. Simultaneously, some accompany the hallucinations and changes in perception that addicts desire; the LSD long-term effects can distress the individual and reduce life quality. The use of the drug can result in significant neurochemistry changes, which can result in changes in personality and the induction of conditions like schizophrenia. It presents the risk of significant injury and even death to self or others and serious consequences when used during pregnancy.
Many LSD side effects can occur even after just a single use of the drug, so it is best to avoid its use completely. It remains a Schedule I substance with significant dangers, so abusers of the drug should seek out help for their problem as soon as they can.
Page Sources
- Friedman SA, Hirsch SE, Extreme Hyperthermia After LSD Ingestion, 1971, https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/article-abstract/339073
- National Institute on Drug Abuse, How Do Hallucinogens Work Affect the Brain and Body, https://www.drugabuse.gov/publications/research-reports/hallucinogens-dissociative-drugs/how-do-hallucinogens-lsd-psilocybin-peyote-dmt-ayahuasca-affect-brain-body
- Hermle L, Simon M, Ruchsow M, Geppert M, Hallucinogen-persisting perception disorder, 2012, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3736944/
- Vardy MM, Kay SR, LSD Psychosis or LSD-Induced Schizophrenia? A Multimethod Inquiry, 1983, https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamapsychiatry/article-abstract/493118
- King W, Ellison G, Long-lasting alterations in behavior and brain neurochemistry following continuous low-level LSD administration, 1989, https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/0091305789904310
- Alcohol and Drug Foundation, LSD, 2020, https://adf.org.au/drug-facts/lsd/
- Rega PP, LSD Toxicity Clinical Presentation, 2019, https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1011615-clinical
- Bouso JC, Dos Santos RG, Alcázar-Córcoles MÁ, Hallak JEC, Serotonergic psychedelics and personality: A systematic review of contemporary research, 2018, https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29452127/
- National Institutes of Health, Protein structure reveals how LSD affects the brain, 2017, https://www.nih.gov/news-events/nih-research-matters/protein-structure-reveals-how-lsd-affects-brain
- Beckley Foundation, The World’s First Images of the Brain on LSD, https://www.beckleyfoundation.org/the-brain-on-lsd-revealed-first-scans-show-how-the-drug-affects-the-brain/
- Zhang L, Dyer DC, Lysergic acid diethylamide is a partial agonist at 5-HT2 receptors in ovine uterine artery of late pregnancy, 1993, https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8428600/
- Alexander GJ, Miles BE, Gold GM, Alexander RB, LSD: Injection Early in Pregnancy Produces Abnormalities in Offspring of Rats, 1967, https://science.sciencemag.org/content/157/3787/459.abstract
- Chan CC, Fishman M, Egbert PR, Multiple ocular anomalies associated with maternal LSD ingestion, 1978, https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/415706/
 Authored by
Authored by  Reviewed by
Reviewed by 
