Benzodiazepines are mostly prescribed for anxiety, sleeping problems, seizures, and other medical conditions. They attach to the GABA-A receptor on neurons to increase the membrane potential, which creates a sedative effect to help the treatment. Ativan (brand name for Lorazepam) belongs to this class. Like any drug, the human body takes some time to completely clear Ativan from the system. In cases of addiction, recovery, or detox, it is important to know how long Ativan stays in your system after taking the last dose.
Table Of Contents:
Lorazepam Half-Life
Ativan is a benzodiazepine that’s used to treat generalized anxiety, insomnia, nausea, and seizures. It’s also used in medical facilities to sedate aggressive patients. According to clinical research, there is an intermediate half-life of Ativan, which is longer than that of Xanax but shorter than that of Valium. The average half-life Ativan is around 12 hours. Although, some studies suggest it could be up to 18 hours.
Note that the primary metabolite of Lorazepam, Lorazepam Glucuronide, has a longer half-life of up to 18 hours.
How Long Do Ativan Effects Last?
Ativan typically lasts for 6-8 hours and is out of the system after 2 to 3 days. The drug’s effects can be felt within 2 hours after administration. The Ativan half-life is between 12 and 18 hours. When taken orally, the drug is absorbed into the gastrointestinal tract. It stays in the body for 2.75 days after the last dose.
Note that Ativan half-life might be affected slightly among individuals based on some factors such as the rate of metabolism, etc.
As stated above, users can feel the initial effects of the drug up to 2 hours after administration. Its effects will typically last for 6 to 8 hours. Most doctors will prescribe 2 to 3 doses a day.
Note that when Ativan is taken intravenously, the drug has a longer duration period.
Although there’s minimal risk of excessive accumulation in the system, Ativan shouldn’t be taken for periods longer than prescribed because it can be habit-forming and may lead to addiction with harmful, even life-threatening, withdrawal symptoms which include (but are not limited to): depression, tension, anxiety, panic attacks, tachycardia, involuntary movements, short term memory loss, numbness of extremities, palpitations, hypersensitivity to light. Once it is completely removed from the body, recovery from the symptoms will gradually start.
Lorazepam Mechanism of Action
Neurons transmit signals or messages throughout the body. When the body is in an anxious state or during seizures, these neurons fire up beyond their usual levels. In order to control this, the body has a natural mechanism in place where GABA (γ-aminobutyric acid) binds to the GABA receptor. In some patients, anxiety can be caused by a reduced level or activity of GABA. The lorazepam mechanism of action somewhat mimics the natural mechanism. Benzodiazepines bind to the GABA-A receptor, also called the benzodiazepine receptor, away from the position where GABA itself attaches and increases its activity.
When a neuron gets an influx of chloride ions, its action is inhibited. The postsynaptic GABA-A ligand-gated chloride channel controls this influx. Benzodiazepines bind to the benzodiazepine receptors on these channels and cause the inhibition of neurons by enabling the influx of chloride ions, which elevates the membrane potential, and the hyperpolarization creates a sedative effect. The inhibitory effect in the amygdala and cerebral cortex is used for anxiety and seizures respectively. It is also used in other conditions where it is important to stop the firing neurons. The Lorazepam mechanism of action is agonistic to GABA.
How Long Does it Take Ativan to Work?
In his 2018 review, David Hui summarized the onset and peak effects of lorazepam with different administration methods. In the case of oral administration, lorazepam takes 2 hours to reach its maximum concentration in the system (Tmax). When administered intramuscularly, this time goes up to 3 hours. When administered sublingually, the time to reach Tmax is only 1 hour. If administered intravenously, it can start its action within 1 to 3 minutes.
Factors that can Influence Ativan Staying in the System
Research shows that the half-life of Ativan is 12 hours. Since after 4-5 half-lives, 94% – 97% of a drug is ideally eliminated from the system, Ativan is typically out of the system after 48 to 60. Allowing for various factors, this time has been observed to be around 72 hours in other studies.
Along with Ativan half-life, various other factors influence how long Ativan can stay in the system:
Individual Physical Factors
The general health and physique of an individual play an important role in how their body responds to a certain drug. This is why physicians use detailed information from checking weight, height, age, etc. before starting a treatment regime. The body’s response also controls the addiction and detox processes.
- Age: Metabolism slows down with age and can contribute to a slower clearance rate of drugs (up to 20% in the case of lorazepam).
- Weight: More body mass means more time needed for the drug to reach Tmax. It also affects the rate of metabolism and hence the clearance rate.
- Genetics: The inherent rate of metabolism of an individual affects his ability to clear out drugs from the system. It also affects how the drug interacts with the system and the time it requires for the drug’s maximum action.
- General health: The general activity, healthy habits, and self-care affect the time it takes for the drug to reach maximum concentration and leave the system, which means it affects the chances of addiction and time required for detox.
Other Factors
- Hydration: Better hydration can increase the clearance of Ativan from the system; the effect is minimal, though.
- Food: Fatty foods slow down a clearance and hence recovery from adverse symptoms.
- Dosage and frequency: The body metabolizes higher doses at a slower pace, which is further slowed down by frequent doses. If drugs are used for longer periods, in frequent or higher doses, they can be deposited in tissues of the body and are gradually cleared over time. Lorazepam half-life can be affected by this, as all the quantity that is not cleared out by the liver will gradually deposit in tissues.
- Administration route: As mentioned earlier in this text, different modes of administration affect the time it takes for the drug to reach the maximum concentration in the system, consequently, the time required for clearance from the system changes as well.
- History of abuse: A history of addiction or abuse can develop drug tolerance, which can interfere with treatment.
- Other drugs: Since it is metabolized in the liver, other drugs processed by the liver can interfere with lorazepam half-life and its clearance hence affecting its detox and recovery (in individuals with a history of abuse). Data shows that alcohol, for example, reduces the clearance rate by 18%. Administrations of probenecid, valproate, and theophylline can alter the lorazepam half-life and its clearance from the system.
Before beginning an Ativan prescription, it’s important to learn more about its side effects, abuse potential, and the possibility of addiction.
It is not advisable to stop the drug abruptly because it could potentially lead to fatal withdrawal symptoms. Always consult a doctor for the proper dosage, course of administration, and other available treatment options.
Ativan on Drug Testing
The durations in which lorazepam is detectable in the system by different tests have been estimated. Lorazepam has also been found in breastmilk but in amounts that do not harm the baby. It can be teratogenic and so female patients should always discuss with their doctors if they are pregnant or trying to be.
How Long Does Ativan Stay in Your Urine?
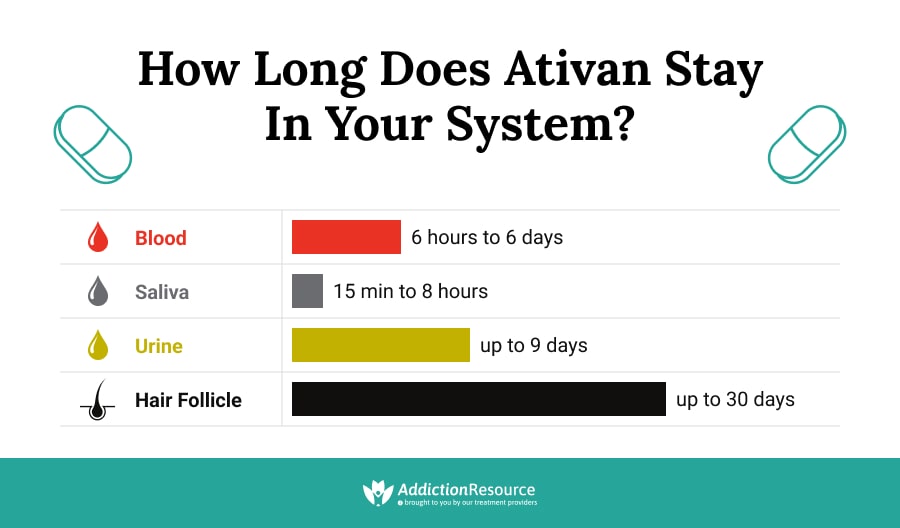
Lorazepam is broken down into its metabolite in the liver and passed out of the body via urine. Short term use of lorazepam can give positive urine test results up to 6 days. Longer use will allow tests to detect its presence in urine even after a week. The residual metabolite lorazepam-glucuronide can show up in the tests after 9 days, even in case of a short term use.
How Long Does Ativan Stay in Your Blood?
Any drug taken by an individual reaches the blood in order to be transported to its target organ. This is why intravenous administration gives the fastest action in the case of most drugs. Blood tests start detecting Ativan after 6 hours, and they would only show the presence of lorazepam for 6 six days.
How Long Does Ativan Stay in Your Saliva?
Saliva test gives the shortest detection window i.e. it is first detectable in oral samples after 15 minutes of the first dose and for up to 8 hours of the last dose.
How Long Does Ativan Stay in Your Hair?
Most chemicals used by an individual are deposited in hair. Although hair samples give the longest window for detection of lorazepam (30 days), they do not start giving results until a week after the first use.
Ativan False Positive
It has been reported that 5 to 10 percent of drug tests done give false positive results. A result is called false positive when an individual has not used a certain drug, but the results show its presence in their system. Several common substances and prescribed medicines can have this effect. It happens when the structure of the tested drug is similar to another medication or its metabolite structure.
When urine tests are done to check for the presence of benzodiazepines in an individual’s system, some prescribed drugs can interfere with the results. Sertraline, an antidepressant, has been reported to give false positives for lorazepam. As are Oxaprozin, a pain medication, Efavirenz, an HIV drug, and other drugs that can interfere with a urine test for benzodiazepines include Tolmetin, Naproxen, Etodolac, and Fenoprofen.
Clearance of Ativan from the System
As with all clinically prescribed drugs, the doctor’s exact dosage and duration to ensure proper treatment should be followed. Once the prescribed or unprescribed (in cases of addiction) use is stopped, the body will take some time to completely clear the medicine from the body, which can vary between individuals. Maintaining general good health can help the process. As said in the beginning, knowing how long Ativan stays in your system will prove beneficial to the patient. The earliest detection time for it in the system is 15 minutes in saliva, and the last traces will be detected in hair for up to a month.
Page Sources
- Greenblatt D. J. Clinical pharmacokinetics of oxazepam and lorazepam. Clinical Pharmacokinetics. 1981; https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/6111408.
- The U.S. Department of Health & Human Services. Lorazepam – Medical Countermeasures Database. 2019. https://chemm.hhs.gov/countermeasure_lorazepam.htm.
- The U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Ativan® CIV (lorazepam) Tablets Rx only. 2007. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2007/017794s034s035lbl.pdf
- University of Rochester Medical Center. Benzodiazepines (Urine). 2020. https://www.urmc.rochester.edu/encyclopedia/content.aspx?contenttypeid=167&contentid=benzodiazepine_urine
- Ghiasi N, Bhansali RK, Marwaha R. Lorazepam. InStatPearls [Internet] 2019. StatPearls Publishing. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK532890/#:~:text=catatonia.%5B3%5D-,Mechanism%20of%20Action,chloride%20ions%20into%20the%20cell.
- Hui D. Benzodiazepines for Agitation in Patients with Delirium: Selecting the Right Patient, Right Time and Right Indication. Current opinion in supportive and palliative care. 2018;12(4):489. https://journals.lww.com/co-supportiveandpalliativecare/Abstract/2018/12000/Benzodiazepines_for_agitation_in_patients_with.16.aspx
- Greenblatt DJ, Schillings RT, Kyriakopoulos AA, Shader RI, Sisenwine SF, Knowles JA, Ruelius HW. Clinical pharmacokinetics of lorazepam. Clinical Pharmacology & Therapeutics. 1976. https://ascpt.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/cpt1976203329
- Hallare J, Gerriets V. Half Life. InStatPearls 2020. StatPearls Publishing. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK554498/
- LORAZEPAM TABLETS, USP CIVRx only. Dailymed.nlm.nih.gov. 2020. Available from: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=a0fbf748-b127-420b-8ad9-5e3e36f82568
- Kintz P, Villain M, Cirimele V, Pépin G, Ludes B. Windows of detection of lorazepam in urine, oral fluid and hair, with a special focus on drug-facilitated crimes. Forensic science international. 2004. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0379073804002427?via%3Dihub
- Falls S, Dakota S. Urine Drug Screening: Minimizing False-Positives and False-Negatives to Optimize Patient Care. US Pharm. 2016;41(8):26-30. https://www.uspharmacist.com/article/urine-drug-screening-minimizing-false-positives-and-false-negatives-to-optimize-patient-care
- Nasky KM, Cowan GL, Knittel DR. False-positive urine screening for benzodiazepines: an association with sertraline?: a two-year retrospective chart analysis. Psychiatry (Edgmont). 2009. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2728940/
- Saitman A, Park HD, Fitzgerald RL. False-positive interferences of common urine drug screen immunoassays: a review. Journal of analytical toxicology. 2014. https://academic.oup.com/jat/article/38/7/387/2798054